A worker pulls a (40.0-mathrm{kg}) crate with a rope, as illustrated in (abla) Figure 5.5. The coefficient
Question:
A worker pulls a \(40.0-\mathrm{kg}\) crate with a rope, as illustrated in \(abla\) Figure 5.5. The coefficient of kinetic (sliding) friction between the crate and the floor is 0.550. If he moves the crate with a constant velocity a distance of \(7.00 \mathrm{~m}\), how much is the work done by the worker on the crate?
THINKING IT THROUGH. A good thing to do first in problems such as this is to draw a free-body diagram. This is shown in the figure. (Frictional forces were covered in Section 4.6 and in general, \(f_{k}=\mu_{\mathrm{k}} N\), where \(N\) is the normal force.) To find the work, the force \(F\) must be known. As usual in such cases, this is done by summing the forces.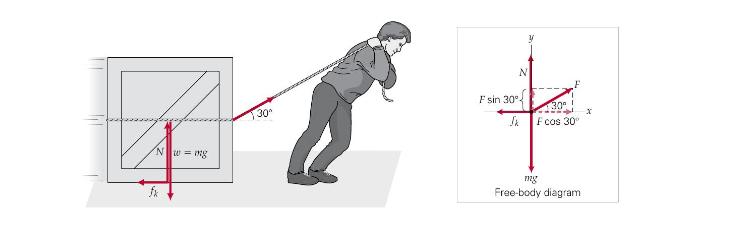
Step by Step Answer:

College Physics Essentials Electricity And Magnetism Optics Modern Physics Volume Two
ISBN: 9781032337272
8th Edition
Authors: Jerry D. Wilson, Anthony J. Buffa, Bo Lou






