Question: A circuit you're building needs an ammeter that goes from (0 mathrm{~mA}) to a full-scale reading of (50.0 mathrm{~mA}). Unfortunately, the only ammeter in the
A circuit you're building needs an ammeter that goes from \(0 \mathrm{~mA}\) to a full-scale reading of \(50.0 \mathrm{~mA}\). Unfortunately, the only ammeter in the storeroom goes from \(0 \mu \mathrm{A}\) to a fullscale reading of only \(500 \mu \mathrm{A}\). Fortunately, you can make this ammeter work by putting it in a measuring circuit, as shown in Figure P23.66. This lets a certain fraction of the current pass through the meter; knowing this value, you cân deduce the total current. Assume that the ammeter is ideal.
a. What value of \(R\) must you use so that the meter will go to full scale when the current \(I\) is \(50.0 \mathrm{~mA}\) ?
b. What is the equivalent resistance of your measuring circuit?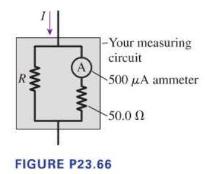
R A -Your measuring circuit 500 A ammeter 50.0 2 FIGURE P23.66
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve this problem lets analyze the circuit shown in Figure P2366 The ammeter is placed in parall... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


