If the balloon rises quickly, so that no heat transfer is possible, the temperature inside the balloon
Question:
If the balloon rises quickly, so that no heat transfer is possible, the temperature inside the balloon will drop as the gas expands. If a \(4.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\) balloon is launched at a pressure of \(100 \mathrm{kPa}\) and rapidly rises to a point where the pressure is \(50 \mathrm{kPa}\), the volume of the balloon will be
A. Greater than \(8.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\).
B. \(8.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
C. Less than \(8.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\).
The data used to generate weather forecasts are gathered by hundreds of weather balloons launched from sites throughout the world. A typical balloon is made of latex and filled with hydrogen.
A packet of sensing instruments (called a radiosonde) transmits? information back to earth as the balloon rises into the atmosphere.
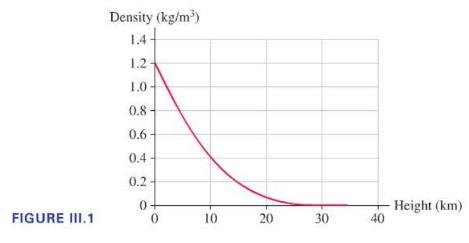
At the beginning of its flight, the average density of the weather balloon package (total mass of the balloon plus cargo divided by their volume) is less than the density of the surrounding air, so the balloon rises. As it does, the density of the surrounding air decreases, as shown in Figure III.1. The balloon will rise to the point at which the buoyant force of the air exactly balances its weight. This would not be very high if the balloon couldn't expand. However, the latex envelope of the balloon is very thin and very stretchy, so the balloon can, and does, expand, allowing the volume to increase by a factor of 100 or more. The expanding balloon displaces an ever-larger volume of the lower-density air, keeping the buoyant force greater than the weight force until the balloon rises to an altitude of \(40 \mathrm{~km}\) or more.
Step by Step Answer:

College Physics A Strategic Approach
ISBN: 9780321907240
3rd Edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight, Brian Jones, Stuart Field





