![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![// index 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 13 int [] numbers = {-30, -9, -6, -4, -2, -1, 0, 2, 4, 10, 12, 17, 22, 30};](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/0/8/5/9445fca2f785f79b1607085943796.jpg)

![7 9 10 11 12 3 // index 13 14 5, 31 8, 15, 18, 22, 39, 40, 42, 50, 57, 71, int[] numbers {-1, 73, 74}; 2.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/0/8/5/8385fca2f0e4621b1607085837751.jpg)


![int [] numbersl = {63, 9, 45, 72, 27, 18, 54, 36}; int[] numbers2 {37, 29, 19, 48, 23, 55, 74, 12};](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/1/7/1085fcdb6744086d1607317106109.jpg)

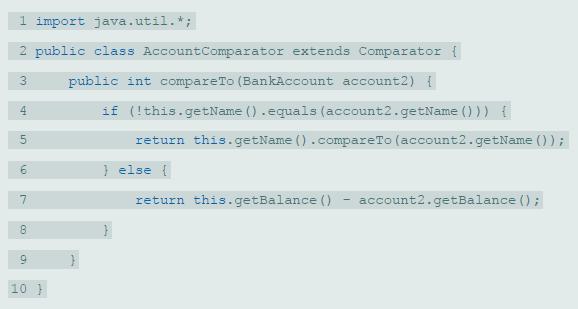
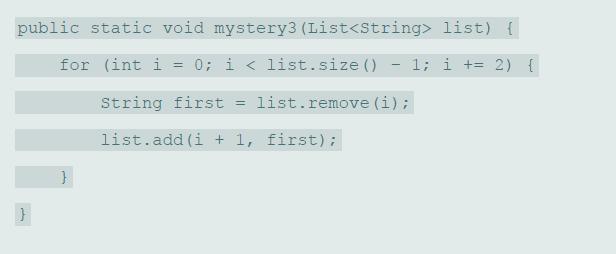
![public static void mystery2 (int [] list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.length / 2; i++) { int j = list.length 1 i; int temp = list[i]; list[i] = list[j]; list[j] temp;](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/1/7/0415fcdb631acbb31607317039474.jpg)
![public static int[] mystery1 (int [] list) { int [] result = new int [2 * list.length]; for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { result[2 * i] list[i] / 2 + list[i] % 2; %3D result[2 * i + 1] list[i] / 2; %3! return result;](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/1/6/9565fcdb5dc144d81607316954188.jpg)
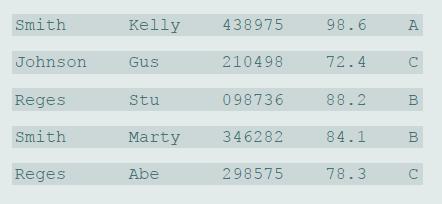
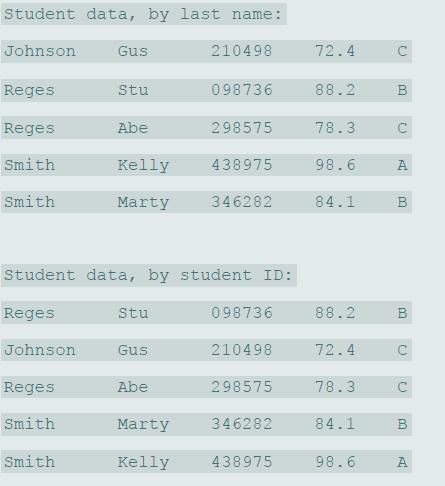
![// index 0 1 2. 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int [] numbers = {0, 5, 10, 15, 40, 55, 60, 65, 70, 80, 85, 90, 95, 300};](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/1/6/8425fcdb56aaa0f91607316841293.jpg)
![// index 0 1 2 4 5 6. 7 9. 10 11 int [] numbers {-1, 3, 8, 15, 18, 22, 39, 40, 42, 50, 57}; 5, 3.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/1/6/8005fcdb540e89241607316799091.jpg)

![a.length-1 2 (a[i] – average(a)²) i=0 stdev (a) : length – 1 а.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1606/9/0/4/5595fc76aef8e5d41606904559691.jpg)