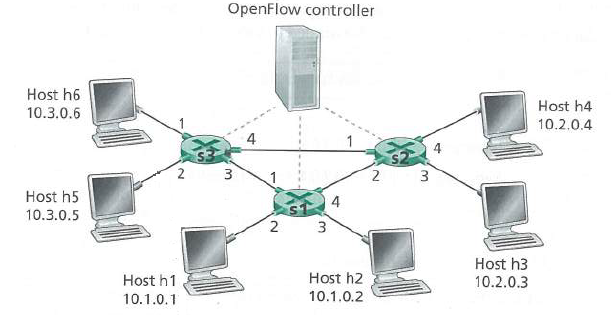
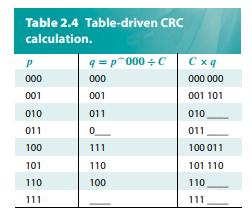
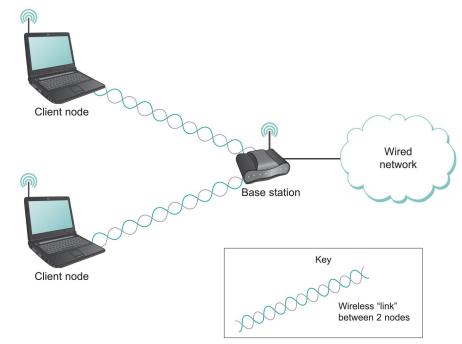
Computer Networks A Systems Approach 6th Edition Larry L. Peterson, Bruce S. Davie - Solutions
Unlock a comprehensive understanding of "Computer Networks A Systems Approach 6th Edition" with our exclusive resources. Access the complete solutions manual and answers key online, providing detailed chapter solutions and step-by-step answers for all questions and solved problems. Whether you're looking for a solution manual, answers, or a test bank, we offer everything you need to master this textbook. Download solutions in PDF format for free and explore the instructor manual for an in-depth insight into network systems. Perfect for students and educators, these resources ensure a thorough grasp of networking concepts.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()