Computing returns on financial assets under fair value accounting Microsoft is the worlds largest computer software company
Question:
Computing returns on financial assets under fair value accounting Microsoft is the world’s largest computer software company and, according to a Financial Times survey in May 2002, the world’s second most valuable company by market capitalisation. Extracts from its 2002 accounts (year ended 30 June) are set out in Exhibit 13.6.
As a US company, Microsoft prepares its accounts according to US GAAP. The accounting for financial investments under US GAAP is similar to that under IAS. Microsoft classifies all shortterm financial investments and most long-term financial investments as ‘available-for-sale securities’
and defers unrealised gains and losses in equity. Equity securities that are not publicly traded are recorded at cost.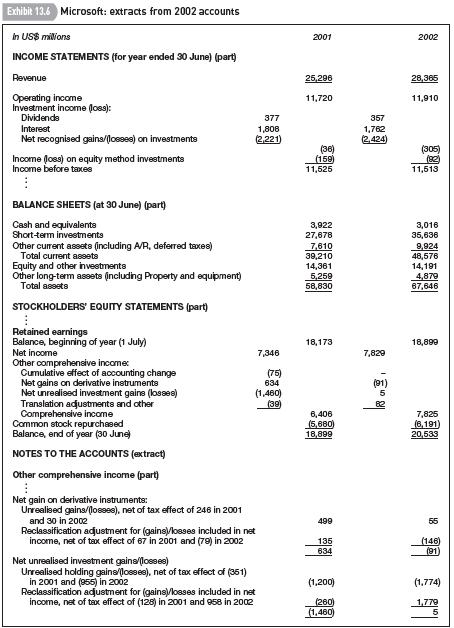
The line item ‘Net recognised gains/(losses) on investments’ in the income statement includes impairment losses, realised gains and losses on disposal of investments, and unrealised losses on derivatives (mainly with respect to those not designated as hedging instruments). Using information in the notes to the accounts, the net recognised gains/(losses) on investments can be broken down as follows (amounts in US$ billions):
Year ended 30 June 2001 2002 Impairment losses (4.80) (4.32)
Realised gains/(losses), equity and other investments 3.00 2.12 Realised gains/(losses), short-term investments 0.17 0.26 Unrealised losses, derivatives (0.59) (0.48)
Net recognised gains/(losses) on investments (2.22) (2.42)
Required
(a) Calculate Microsoft’s pre-tax financial income on a fair value basis for 2001 and 2002 (i.e. include investment-related unrealised gains and losses arising in the year).
(b) After reviewing the accounts for 2001 and 2002, an analyst remarks: ‘Microsoft’s financial performance is being adversely affected by the poor returns it’s earning on its investments.’ Calculate the company’s return on total assets, return on operating assets (ROOA) and return on financial assets (ROFA) for both years. ROOA and ROFA are defined as follows: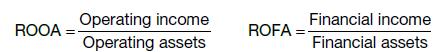
Use pre-tax income numbers in the numerator and end-year asset figures in the denominator of the ratios. Assume financial income (and therefore total income) is computed on a fair value basis.
Assume also that financial assets consist of short-term investments and equity and other investments and all other assets are operating assets. Comment on the ratios you’ve calculated. Is the analyst correct? What do you think Microsoft’s response might be – to the analyst’s comments and to your calculations?AppenedixLO1
Step by Step Answer:






