Investments and insurance companies: impact of stock market decline Allianz is Germanys and Europes largest
Question:
Investments and insurance companies: impact of stock market decline Allianz is Germany’s – and Europe’s – largest insurance group. Premiums earned exceeded A50 billion in 2001 and total assets were almost A1,000 billion at the end of that year. Yet the group experienced difficulties throughout 2001 and 2002. Its banking unit, Dresdner Bank, which it acquired in 2001, made losses in both years. Its main property and casualty insurance business was hit hard – by asbestos claims in the USA and flood damage claims in central Europe. And the decline in the stock market wiped off billions of euros from its investment portfolio.
The group’s problems are reflected in its annual 2001 and interim 2002 financial statements. Return on equity fell from 10.6% in 2000 to 4.8% in 2001, below the cost of equity capital. Performance continued to be weak in the first half of 2002. Operating cash flow was negative in that period and the parent company made a loss in the second quarter. The company’s equity base was further eroded by the decline in share prices. Shareholders’ equity (of the parent company) fell A3 billion (to A28.7 billion)
in the first half of 2002: unrealised investment losses more than offset the small retained income in the period. Exhibit 13.7 gives a breakdown of the group’s investments at end-December 2001 and end-
June 2002 and shows the change in unrealised gains on equity investments between December 2000 and June 2002. (Allianz prepares its accounts according to IAS.)
In September 2002 Allianz was forced to deny reports that it needed to raise new equity capital to support its business. At the time its share price was A100, down from A400 at the end of 2000.
Required
(a) Analyst A reckons that Allianz has no need to raise new equity. The group can simply sell some of its investments. By doing this, it would raise cash and increase shareholders’ equity – since the realised gains would boost profits. Is the analyst’s reasoning correct? If not, explain why.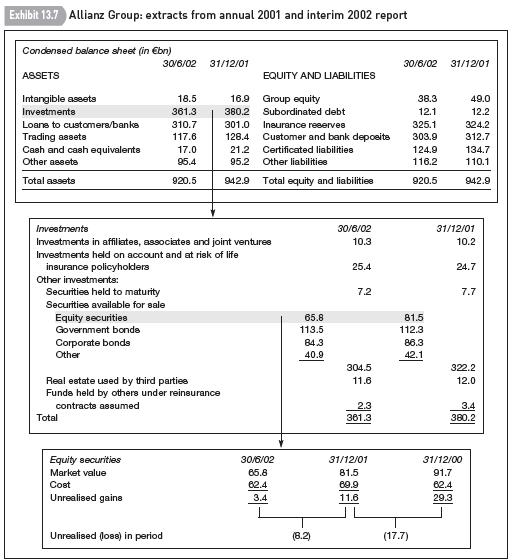
(b) Analyst B notes that the company’s market capitalisation in September 2002 is below the fair value of its principal listed equity investments (as set out in the notes to the annual accounts).
In B bn Sept 2002 End-Dec 2001 Market capitalisation 26 64 Listed equity investments 36 (estimate) 55 (MV ≥ A100m or % stake ≥ 5%)
The analyst considers the company is vulnerable to a takeover bid since it is trading on a price-tobook ratio of less than one. A bidder could buy the company, sell the listed investments and earn a profit on its investment. Comment on this argument. What are the assumptions the analyst is making?AppenedixLO1
Step by Step Answer:






