(Standards revision) NuLathe Company produces a component for aircraft man ufacturers. A standard cost system has been...
Question:
(Standards revision) NuLathe Company produces a component for aircraft man¬ ufacturers. A standard cost system has been used for years with good results. Unfortunately, NuLathe’s original direct material source went out of business. The new source produces a similar but higher quality material. The price per pound from the original source averaged $7; the price from the new source is $7.77. The new material reduces scrap and, thus, reduces the use of direct ma¬ terial from 1.25 to 1.00 pounds per unit. In addition, direct labor is reduced from 24 to 22 minutes per unit because there is less scrap labor and machine setup time.
The direct material problem was occurring at the same time that labor negotiations resulted in an increase of over 14 percent in hourly direct labor costs. The average rate rose from $12.60 per hour to $14.40 per hour. Produc¬ tion of the main product requires a high level of labor skill. Because of a con¬ tinuing shortage in that skill area, an interim wage agreement had to be signed.
NuLathe started using the new direct material on April 1, the same date that the new labor agreement went into effect. However, the company is still using standards that were set at the beginning of the calendar year. The direct material and direct labor standards for the turbo engine component are as follows:
Howard Foster, cost accounting supervisor, had been examining the follow¬ ing April 30 performance report.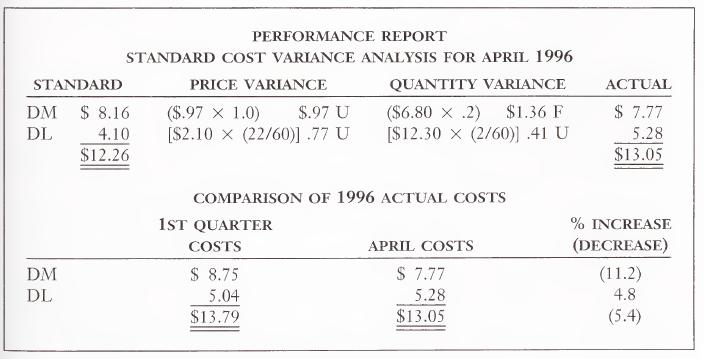
Jane Keene, assistant controller, came into Foster’s office and Foster said, “Jane, look at this performance report! Direct material price increased 11 per¬ cent and the labor rate increased over 14 percent during April. I expected greater variances, yet prime costs decreased over 5 percent from the $13.79 we experi¬ enced during the first quarter of this year. The proper message just isn’t coming through.”
“This has been an unusual period,” said Keene. “With all the unforeseen changes, perhaps we should revise our standards based on current conditions and start over.”
Foster replied, “I think we can retain the current standards but expand the variance analysis. We could calculate variances for the specific changes that have occurred to direct material and direct labor before we calculate the normal price and quantity variances. What I really think would be useful to management right now is to determine the impact the changes in direct material and direct labor had in reducing our prime costs per unit from $13.79 in the first quarter to $13.05 in April—a reduction of $.74.”
a. Discuss the advantages of (1) immediately revising the standards and (2) re¬ taining the current standards and expanding the analysis of variances.
b. Prepare an analysis that reflects the impact of the new direct material and new labor contract on reducing NuLathe’s prime costs per unit from $13.79 to $13.05. The analysis should show the changes in prime costs per unit that are caused by (1) the use of new direct materials and (2) the new labor contract. This analysis should be in sufficient detail to identify the changes due to direct material price, direct labor rate, the effect of direct material quality on direct material usage, and the effect of direct material quality on direct labor usage.
(CMA adapted)LO1
Step by Step Answer:

Cost Accounting Traditions And Innovations
ISBN: 9780538880473
3rd Edition
Authors: Jesse T. Barfield, Cecily A. Raiborn, Michael R. Kinney





