Protein A binds to protein B to form a complex, AB. At equilibrium in a cell the
Question:
Protein A binds to protein B to form a complex, AB. At equilibrium in a cell the concentrations of A, B, and AB are all at 1 μM.
A. Referring to Figure 3−19, calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction A + B ↔ AB.
B. What would the equilibrium constant be if A, B, and AB were each present in equilibrium at the much lower concentrations of 1nM each?
C. How many extra hydrogen bonds would be needed to hold A and B together at this lower concentration so that a similar proportion of the molecules are found in the AB complex?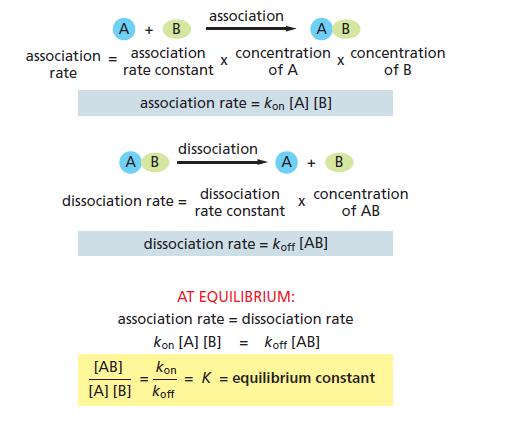
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Essential Cell Biology
ISBN: 9780393680362
5th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Karen Hopkin, Alexander Johnson, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Question Posted:





