Question:
Harley-Davidson, Inc. provides the following footnote in its 2012 10-K report relating to the securitization of receivables by its finance subsidiary, Harley-Davidson Financial Services (HDFS).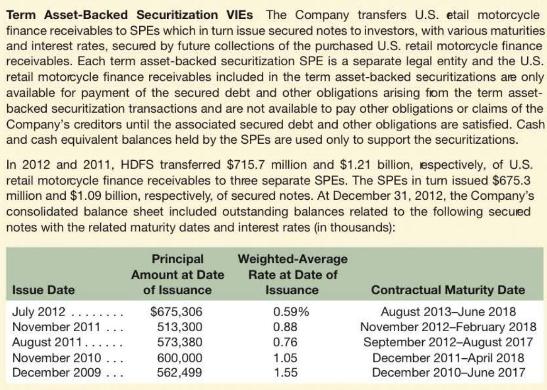
a. Describe in your own words, the securitization process employed by HDFS.
b. What benefits does Harley-Davidson derive by securitizing receivables in this manner?
c. Current accounting standards require consolidation of the VIEs. What effect does this have on Harley-Davidson? Is there still a benefit to securitization? Explain.
Transcribed Image Text:
Term Asset-Backed Securitization VIES The Company transfers U.S. etail motorcycle finance receivables to SPEs which in turn issue secured notes to investors, with various maturities and interest rates, secured by future collections of the purchased U.S. retail motorcycle finance receivables. Each term asset-backed securitization SPE is a separate legal entity and the U.S. retail motorcycle finance receivables included in the term asset-backed securitizations are only available for payment of the secured debt and other obligations arising from the term asset- backed securitization transactions and are not available to pay other obligations or claims of the Company's creditors until the associated secured debt and other obligations are satisfied. Cash and cash equivalent balances held by the SPES are used only to support the securitizations. In 2012 and 2011, HDFS transferred $715.7 million and $1.21 billion, respectively, of U.S. retail motorcycle finance receivables to three separate SPES. The SPES in tum issued $675.3 million and $1.09 billion, respectively, of secured notes. At December 31, 2012, the Company's consolidated balance sheet included outstanding balances related to the following secured notes with the related maturity dates and interest rates (in thousands): Issue Date July 2012 November 2011 August 2011... November 2010 December 2009 Principal Amount at Date of Issuance $675,306 513,300 573,380 600,000 562,499 Weighted-Average Rate at Date of Issuance 0.59% 0.88 0.76 1.05 1.55 Contractual Maturity Date August 2013-June 2018 November 2012-February 2018 September 2012-August 2017 December 2011-April 2018 December 2010-June 2017








