Suppose the vertical pipe of Prob. 10112 is now horizontal instead. In order to achieve the same
Question:
Suppose the vertical pipe of Prob. 10–112 is now horizontal instead. In order to achieve the same volume flow rate as that of Prob. 10–112, we must supply a forced pressure gradient. Calculate the required pressure drop between two axial locations in the pipe that are the same distance apart as z2 and z1 of Fig. P10–112. How does modified pressure P´ change between the vertical and horizontal cases?
Data from Problem 112
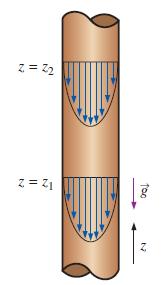
Water falls down a vertical pipe by gravity alone. The flow between vertical locations z1 and z2 is fully developed, and velocity profiles at these two locations are sketched in Fig. P10–112. Since there is no forced pressure gradient, pressure P is constant everywhere in the flow (P = Patm). Calculate the modified pressure at locations z1 and z2. Sketch profiles of modified pressure at locations z1 and z2. Discuss.
FIGURE P10–112
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala




