The Adams Corporation makes standard-size 2-inch fasteners , which it sells for $155 per thousand. Mr. Adams
Question:
January...............$263,500 (1 ,700,000 fasteners)
February.............$186,000 (1 ,200,000 fasteners)
March.................$217,000 (1 ,400,000 fasteners)
April...................$31 0,000 (2 ,000,000 fasteners)
May.....................$387,500 (2 ,500,000 fasteners)
Last year, Adams Corporation's sales were $175,000 (1 ,129,030 fasteners) in November and $232,500 (1,500,000 fasteners) in December. Mr. Adams is preparing for a meeting with his banker to arrange the financing for the first quarter. Based on his sales forecast and the following information provided by him, your job as his new financial analyst is to prepare a monthly cash budget, a monthly and quarterly pro forma income statement, a pro forma quarterly balance sheet, and all necessary supporting schedules for the first quarter.
Past history shows that Adams Corporation collects 50 percent of its accounts receivable in the normal 30-day credit period (the month after the sale) and the other 50 percent in 60 days (two months after the sale). It pays for its materials 30 days after receipt. In general, Mr. Adams likes to keep a two-month supply of inventory on hand in anticipation of sales. Inventory at the beginning of December was 2,600,000 units. (This was not equal to his desired two-month supply.)
The major cost of production is the purchase of raw materials in the form of steel rods that are cut, threaded, and finished. Last year raw material costs were $52 per 1,000 fasteners, but Mr. Adams has just been notified that material costs have increased, effective January 1, to $60 per 1,000 fasteners. The Adams Corporation uses FIFO inventory accounting. Labour costs are relatively constant at $20 per thousand fasteners, since workers are paid on a piecework (per unit) basis. Overhead is allocated at $10 per thousand units, and selling and administrative expense is 20 percent of sales. Labour expense and overhead are direct cash outflows paid in the month incurred, while interest and taxes are paid quarterly.
The corporation usually maintains a minimum cash balance of $25,000, and it invests its excess cash into marketable securities. The average tax rate is 40 percent, and Mr. Adams usually pays out 50 percent of net income in dividends to shareholders. Marketable securities are sold before funds are borrowed when a cash shortage occurs. Ignore the interest on any short-term borrowings. Interest on the long-term debt, taxes, and dividends are paid in March.
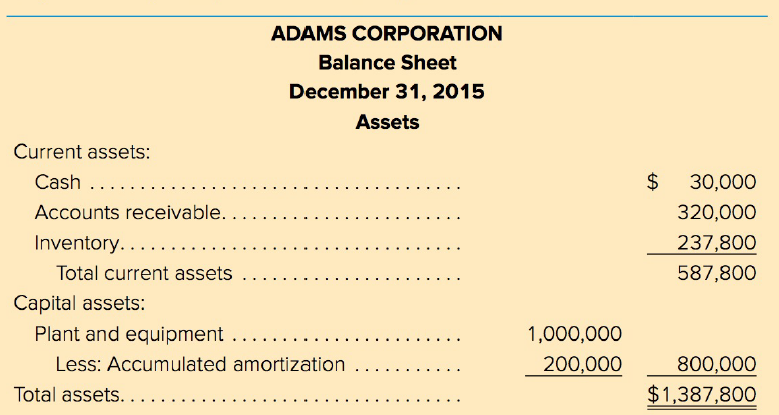
Liabilities and Shareholders' .............................Equity
Accounts payable............................................$ 93,600
Notes payable .................. . ........................................0
Long-term debt, 8 percent.................................400,000
Common stock..................................................504,200
Retained earnings ......................... . . ..............390,000
Total liabil ities and shareholders' equity......$1,387,800
Step by Step Answer:

Foundations of Financial Management
ISBN: 978-1259024979
10th Canadian edition
Authors: Stanley Block, Geoffrey Hirt, Bartley Danielsen, Doug Short, Michael Perretta





