Inventory Costing and LCNRV} J&J Enterprises sells paper cups to fast-food franchises. On January 1, 2018, J&J
Question:
Inventory Costing and LCNRV}
J\&J Enterprises sells paper cups to fast-food franchises. On January 1, 2018, J\&J had 5,000 cups on hand, for which it had paid \(\$ 0.10\) per cup. During 2018 , J\&J made the following purchases and sales:
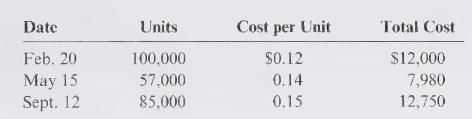
During 2018, J\&J sold 240,000 cups at \(\$ 0.35\) per cup \((80,000\) cups were sold on April 2 and 160,000 cups were sold on October 20), leaving an ending inventory of 7,000 cups. Assume that \(\mathrm{J} \& \mathrm{~J}\) uses a perpetual inventory system. \(\mathrm{J} \& \mathrm{~J}\) uses the lower of cost or net realizable for its inventories, as required by GAAP and IFRS.
\section*{Required:}
1. Assume that the net realizable value of the cups is \(\$ 0.38\) per cup on December 31,2018 . Compute the cost of ending inventory using the FIFO and weighted average cost methods and then apply LCNRV. (Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)
2. Assume that the net realizable value of the cups is \(\$ 0.12\) per cup on December 31, 2018 . Compute the cost of ending inventory using the FIFO and weighted average cost methods and then apply LCNRV. (Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)
Problem
Step by Step Answer:

Cornerstones Of Financial Accounting
ISBN: 9780176707125
2nd Canadian Edition
Authors: Jay Rich, Jefferson Jones, Maryanne Mowen, Don Hansen, Donald Jones, Ralph Tassone





