A flat plate coated with a volatile substance (species A) is exposed to dry, atmospheric air in
Question:
A flat plate coated with a volatile substance (species A) is exposed to dry, atmospheric air in parallel flow with T∞ = 20°C and u∞ = 8 m/s. The plate is maintained at a constant temperature of 134°C by an electrical heating element, and the substance evaporates from the surface. The plate has a width of 0.25 m (normal to the plane of the sketch) and is well insulated on the bottom.
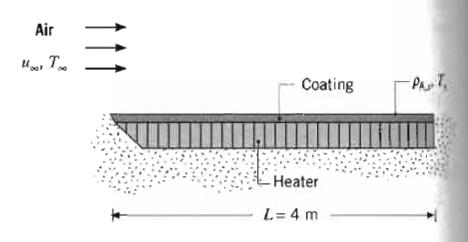 The molecular weight and the latent heat of vaporization of species A are MA = 150 kg/kmol and hfg = 5.44 × 100 J/kg, respectively, and the mass diffusivity is DAB = 7.75 × 10 m/s. If the saturated vapor pressure of the substance is 0.12 atm at 134°C, what is the electrical power required to maintain steady-state conditions?
The molecular weight and the latent heat of vaporization of species A are MA = 150 kg/kmol and hfg = 5.44 × 100 J/kg, respectively, and the mass diffusivity is DAB = 7.75 × 10 m/s. If the saturated vapor pressure of the substance is 0.12 atm at 134°C, what is the electrical power required to maintain steady-state conditions?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





