Question:
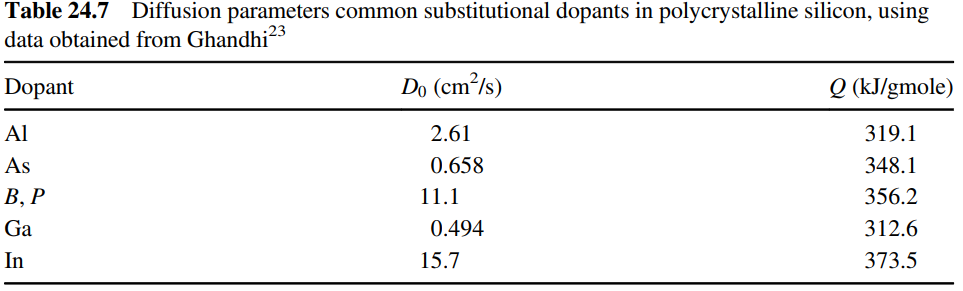
Aluminum is the primary conductor material for fabrication of microelectronic devices. Consider the composite thin film shown in the figure below. A thin film of solid aluminum is sputter-coated onto a wafer surface. Then, a 0.50-μm thin film of silicon is added on top of the aluminum film by chemical vapor deposition of silane. If a high temperature is maintained during subsequent processing steps, then the aluminum can diffuse into the Si thin film and change the characteristics of the microelectronic device. Estimate the concentration of Al halfway into the Si thin film if the temperature is maintained at 1250 K for 10 h. Consider whether or not the process represents diffusion within a semi-infinite medium or in a finite-dimensional medium. At 1250 K, the maximum solubility of Al in Si is about 1 wt%. Solid-phase diffusivity data for common dopants in silicon are provided in Figure 24.12 and Table 24.7.

Figure 24.12
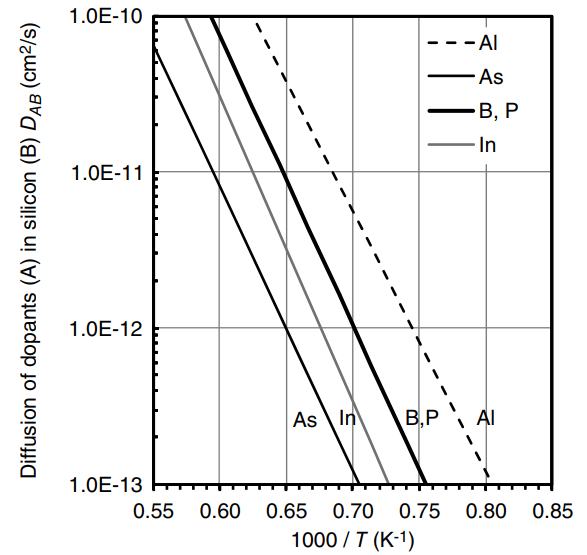
Table 24.7
Transcribed Image Text:
NA Silicon thin film (0.5 µm) Aluminum thin film (species A) Wafer surface 1.0E-10 --- AI ·As B, P - In 1.0E-11 1.0E-12 As \ In B.P AI 1.0E-13 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 1000 / T (K-1) Diffusion of dopants (A) in silicon (B) DAB (cm2/s)










