Question:
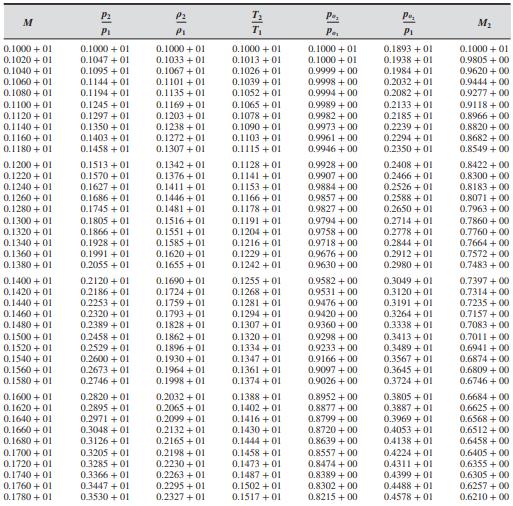
The reflected shock wave associated with a given incident shock can be calculated strictly from the use of Table A.2, without using Eq. (7.23). However, the use of Table A. 2 for this case requires a trial-and-error solution, converging on the proper boundary condition of zero mass motion behind the reflected shock wave. Repeat Prob. 7.5, using Table A. 2 only.
Data From Problem 7.5:
Consider an incident normal shock wave that reflects from the endwall of a shock tube. The air in the driven section of the shock tube (ahead of the incident wave) is at \(p_{1}=0.01 \mathrm{~atm}\) and \(T_{1}=300 \mathrm{~K}\). The pressure ratio across the incident shock is 1050.
Table A.2:
Transcribed Image Text:
M 0.1000+01 0.1020 +01 Pi 0.1000+01 0.1047+01 al M Pi Pi 0.1000+01 0.1033+01 0.1000+01 0.1013 +01 0.1040 +01 0.1095 +01 0.1067 +01 0.1026 +01 0.1060 +01 0.1144 +01 0.1101 +01 0.1080+01 0.1194 +01 0.1135+01 0.1100+01 0.1245 +01 0.1169+01 0.1039 +01 0.1052+01 0.1065 +01 0.1000+01 0.1000+01 0.9999+00 0.9998+00 0.1893 +01 0.1000+01 0.1938 +01 0.9805+00 0.9994 +00 0.9989+00 0.1120+01 0.1297 +01 0.1203 +01 0.1078 +01 0.1140+01 0.1350+01 0.1238+01 0.1090 +01 0.1160+01 0.1403 +01 0.1272 +01 0.1103+01 0.9982+00 0.9973+00 0.9961+00 0.1984 +01 0.2032+01 0.2082 +01 0.2133+01 0.2185 +01 0.9620+00 0.9444+00 0.9277 +00 0.9118+00 0.8966+00 0.1180+01 0.1458 +01 0.1307+01 0.1115+01 0.9946+00 0.2239 +01 0.2294 +01 0.2350+01 0.8820+00 0.8682 +00 0.8549 +00 0.1200+01 0.1513 +01 0.1342+01 0.1128+01 0.9928+00 0.2408 +01 0.8422 +00 0.1220+01 0.1570 +01 0.1376+01 0.1141 +01 0.9907+00 0.2466 +01 0.8300+00 0.1240+01 0.1627+01 0.1411+011 0.1153 +01 0.9884+00 0.2526 +01 0.8183+00 0.1260+01 0.1686+01 0.1446+01 0.1166 +01 0.9857+00 0.2588 +01 0.8071 +00 0.1280+01 0.1745 +01 0.1481+01 0.1178 +01 0.9827+00 0.2650 +01 0.7963+00 0.1300+01 0.1805+01 0.1516+01 0.1191 +01 0.9794 +00 0.2714 +01 0.7860+00 0.1320+01 0.1866 +01 0.1551+01 0.1204 +01 0.9758+00 0.2778 +01 0.7760+00 0.1340 +01 0.1928+01 0.1585+01 0.1216 +01 0.9718+00 0.2844 +01 0.7664 +00 0.1360+01 0.1991 +01 0.1620+01 0.1229 +01 0.9676+00 0.1380+01 0.1400+01 0.2055 +01 0.1655+01 0.1242 +01 0.9630+00 0.2912+01 0.2980+01 0.2120+01 0.1690+01 0.1255+01 0.1420+01 0.2186 +01 0.1724 +01 0.1268 +01 0.9582+00 0.9531+00 0.1440 +01 0.2253 +01 0.1759+01 0.1281 +01 0.9476+00 0.1460 +01 0.2320 +01 0.1793 +01 0.1294 +01 0.9420+00 0.3049 +01 0.3120+01 0.3191 +01 0.3264 +01 0.7572 +00 0.7483+00 0.7397 +00 0.7314+00 0.7235+00 0.7157+00 0.1480+01 0.2389 +01 0.1828+01 0.1307+01 0.9360+00 0.3338+01 0.7083+00 0.1500+01 0.2458 +01 0.1862+01 0.1320+01 0.9298+00 0.3413 +01 0.7011+00 0.1520+01 0.2529 +01 0.1896 +01 0.1334 +01 0.9233+00 0.3489 +01 0.6941+00 0.1540+01 0.2600+01 0.1930+01 0.1560 +01 0.2673 +01 0.1964 +01 0.1347+01 0.1361 +01 0.9166+00 0.3567 +01 0.6874 +00 0.9097+00 0.1580+01 0.2746+01 0.1998+01 0.1374 +01 0.9026+00 0.3645+01 0.3724 +01 0.1600+01 0.2820+01 0.2032+01 0.1388 +01 0.8952+00 0.3805 +01 0.1620+01 0.1640 +01 0.2895 +01 0.1660+01 0.1680 +01 0.2971 +01 0.3048 +01 0.3126+01 0.1700+01 0.3205+01 0.1720+01 0.3285 +01 0.1740+01 0.3366 +01 0.1760 +01 0.3447+01 0.1780+01 0.3530+01 0.2065 +01 0.2099 +01 0.2132+01 0.2165 +01 0.2198 +01 0.2230+01 0.2263 +01 0.2295 +01 0.2327+01 0.1444 +01 0.1458+01 0.1473 +01 0.1487 +01 0.1502+01 0.1517+01 0.1402+01 0.8877+00 0.3887 +01 0.6809+00 0.6746+00 0.6684 +00 0.6625+00 0.1416+01 0.8799+00 0.3969 +01 0.6568+00 0.1430+01 0.8720+00 0.4053 +01 0.6512+00 0.8639+00 0.4138 +01 0.6458+00 0.8557 +00 0.4224 +01 0.6405+00 0.8474+00 0.4311 +01 0.6355+00 0.8389+00 0.4399 +01 0.6305+00 0.8302+00 0.4488 +01 0.6257+00 0.8215+00 0.4578 +01 0.6210+00








