This problem expands upon Example 15-4. A reaction vessel is rigid and has a volume of 500
Question:
This problem expands upon Example 15-4. A reaction vessel is rigid and has a volume of 500 L and initially contains 10 moles of o-xylene. The liquid phase is exposed to catalyst that facilitates isomerization reactions between the three isomers of xylene, but it is realistic to assume no reactions occur in the vapor phase. The liquid phase can be modeled as an ideal solution, and the vapor phase can be modeled as an ideal gas.
A. The contents of the vessel are allowed to reach equilibrium at 100°C. Find the pressure, and the contents of the liquid, and the vapor phase at equilibrium.
B. The contents of the vessel are cooled from the 100°C equilibrium state to 75°C, and a new equilibrium state is established at 75°C. Find the new pressure and the contents of the liquid and vapor phase. Also determine the amount of heat that was removed.
C. The vessel is at the equilibrium state described in part B when 5 kJ of heat are added to the vessel and the vessel is again allowed to reach equilibrium. Find the new pressure, temperature, and contents of the liquid and vapor phases.
Example 15-4.
The three isomers of xylene are o-xylene, m-xylene, and p-xylene (standing for “ortho,” “meta,” and “para”) shown in Figure 15-4.
Inter-conversions between these isomers can be modeled through these two chemical reactions:
(R1): o-xylene ↔ m-xylene
(R2): m-xylene ↔ p-xylene
A. 10 moles of xylene are placed in a vessel that is maintained at T = 100°C and P = 1 atm. Find the amounts of o-, p-, and m-xylene that are present at equilibrium.
B. 10 moles of xylene are placed in a vessel that is maintained at T = 100°C and has a volume of 600 L. The vessel contains both liquid and vapor. The liquid phase is exposed to a catalyst but the vapor is not; thus we can assume reactions R1 and R2 attain equilibrium in the liquid phase but do not occur at all in the vapor phase. Find the contents of the reactor at equilibrium..
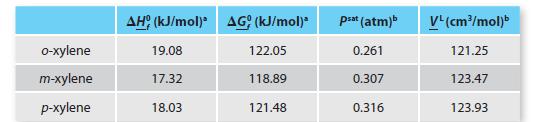
We will use the following data, which uses T = 25°C and P 5 1 atm, rather than P = 1 bar, as a reference state
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781111580704
1st Edition
Authors: Kevin D. Dahm, Donald P. Visco





