A pipeline containing natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains 80% methane gas (CH 4 ,
Question:
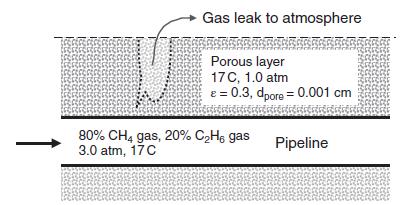
A pipeline containing natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains 80% methane gas (CH4, species A) and 20% ethane (C2H6, species B) gas at 3.0 atm and 17 C, as shown in figure below. We are concerned that if the pipeline leaks, then the gas mixture can transfer through the porous layer above the pipeline and ultimately escape to the atmosphere. As part of this analysis, it will be necessary to estimate the effective diffusion coefficient of methane and ethane through the porous material. Additional information: porous layer, ε = 0.3, dpore = 0.0010 cm, MA = 16 g/gmole, MB = 30 g/g mole.
a. What is the molar concentration of ethane (B) gas inside the pipeline?
b. What is the molecular diffusion coefficient of methane gas (CH4, species A) in ethane gas (C2H6, species B) inside the pipe at (P = 3.0 atm) by the Fuller–Schettler–Giddings approach?
c. What is the effective diffusion coefficient of methane in the methane/ethane gas mixture through the porous layer (D’Ae), assuming the gas space inside the porous layer is at 1.0 atm (P = 1.0 atm)? You may assume that the gas space in the porous layer contains only methane and ethane.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119723547
7th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





