Natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) gas that will be
Question:
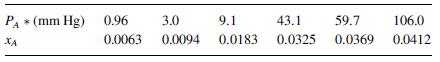
Natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas that will be removed by absorption into a specialty solvent through an interphase mass transfer process. In the present process, the gas contains 6.0 mole% H2S and the liquid solvent contains 2.0 mole% H2S. The methane carrier gas is not soluble in the solvent, and the solvent is nonvolatile. The process is maintained at 2.0 atm and 40 C, and at these conditions, the equilibrium distribution curve data for H2S in the solvent is given in the table below. The average molar concentration of the specialty solvent is 49.6 kgmole/m3. The film mass transfer coefficient for the gas phase based on the mole fraction driving force is ky = 0.040 gmole/m2s, and overall mass transfer coefficient based on the gas phase mole fraction driving force is Ky 0.030 gmole/m2s.
a. What are yA*and xA*? Plot out on an y-x diagram.
b. What are the gas-liquid interface compositions, in terms of yA,i and xA,i? Plot out on an y-x diagram.
c. What is the overall mass transfer coefficient based on the gas phase partial pressure driving force, KG?
d. What is the flux of H2S from the bulk gas to the bulk liquid?
Equilibrium distribution data for H2S in the solvent at 40 C are given in the table below.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119723547
7th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





