Consider a stationary plasma (electrons and one type of ions) under steady-state conditions at a uniform temperature
Question:
Consider a stationary plasma (electrons and one type of ions) under steady-state conditions at a uniform temperature T0 , when perturbed by a point charge +Q placed at the origin of a coordinate system. Using the collisionless hydrodynamic equation for the electrons and ions (α = e, i)
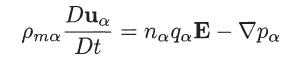
with the ideal gas law Pα = nαkT0, and the Poisson equation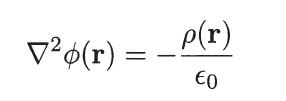
obtain the following differential equation
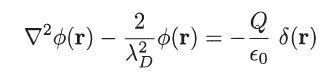
for the Debye potential ϕ(r). Assume that the number density of each species can be expressed as nα = n0 + n′α, where n0 is constant and |n′α | ≪ n0. What are the approximations necessary to obtain this result?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





