The airwater counterflowing heat exchanger given in Problem 4.95 has an air exit temperature of 360 K.
Question:
The air–water counterflowing heat exchanger given in Problem 4.95 has an air exit temperature of 360 K. Suppose the air exit temperature is listed as 300 K; then a ratio of the mass flow rates is found from the energy equation to be 5. Show that this is an impossible process by looking at air and water temperatures at several locations inside the heat exchanger. Discuss how this puts a limit on the energy that can be extracted from the air.
Data from Problem 4.95
A heat exchanger, shown in Fig. P4.95, is used to cool an air flow from 800 to 360 K, with both states at 1 MPa. The coolant is a water flow at 15◦C, 0.1 MPa. If the water leaves as saturated vapor, find the ratio of the flow rates m˙ water/m˙ air.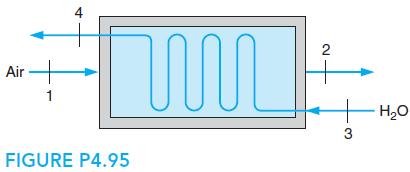
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781118131992
8th Edition
Authors: Claus Borgnakke, Richard E. Sonntag





