Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that occurs in many organisms and facilitates the interconversion between alcohols
Question:
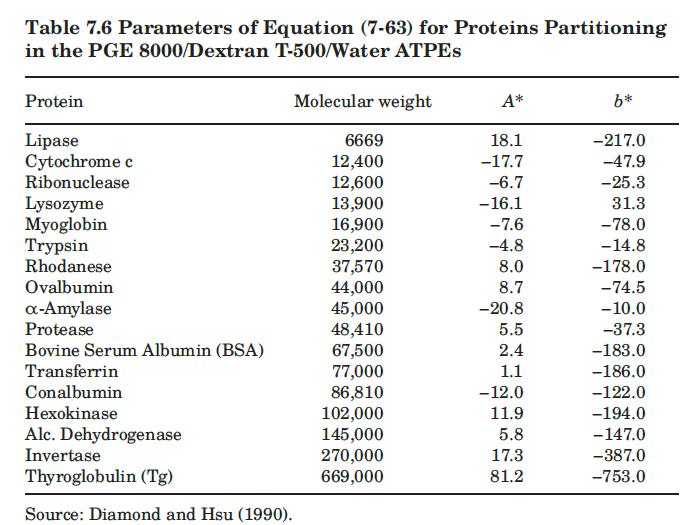
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that occurs in many organisms and facilitates the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide \(\left(\mathrm{NAD}^{+}\right)\)to NADH. In humans and many other animals, it serves to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic. Consider the partitioning of ADH in the PEG 8000/dextran T-500/water ATPE system at \(4{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). One tie line for this system-in terms of wt\% for PEG, dextran, and water-shows a top-phase composition of 7.1, 0.9, and 92.0, with a bottom-phase composition of 1.1, 13.9, and 85.0. Calculate the partition coefficient for ADH under these conditions using information from Table 7.6.
Data From Table 7.6:-
Step by Step Answer:






