Latent heat capsules consist of a thin-walled spherical shell within which a solid-liquid, phase-change material (PCM) of
Question:
Latent heat capsules consist of a thin-walled spherical shell within which a solid-liquid, phase-change material (PCM) of melting point \(T_{\mathrm{mp}}\) and latent heat of fusion \(h_{s f}\) is enclosed. As shown schematically, the capsules may be packed in a cylindrical vessel through which there is fluid flow. If the PCM is in its solid state and \(T_{\mathrm{mp}}
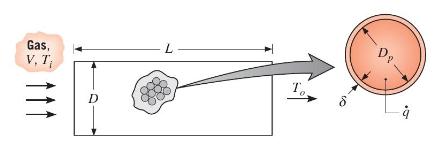
Consider an application for which air at atmospheric pressure is chilled by passing it through a packed bed \((\varepsilon=0.5)\) of capsules \(\left(D_{c}=50 \mathrm{~mm}\right)\) containing an organic compound with a melting point of \(T_{\mathrm{mp}}=4^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The air enters a cylindrical vessel \(\left(L_{v}=D_{v}=0.40 \mathrm{~m}\right)\) at \(T_{i}=\) \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(V=1.0 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\).
(a) If the PCM in each capsule is in the solid state at \(T_{\mathrm{mp}}\) as melting occurs within the capsule, what is the outlet temperature of the air? If the density and latent heat of fusion of the PCM are \(ho=1200 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\) and \(h_{s f}=165 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg}\), what is the mass rate \((\mathrm{kg} / \mathrm{s})\) at which the PCM is converted from solid to liquid in the vessel?
(b) Explore the effect of the inlet air velocity and capsule diameter on the outlet temperature.
(c) At what location in the vessel will complete melting of the PCM in a capsule first occur? Once complete melting begins to occur, how will the outlet temperature vary with time and what is its asymptotic value?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119220442
8th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine





