The activated carbon leaving the adsorber of Problem 3.17 is regenerated by countercurrent contact with steam at
Question:
The activated carbon leaving the adsorber of Problem 3.17 is regenerated by countercurrent contact with steam at $380 \mathrm{~K}$ and $1 \mathrm{~atm}$. The regenerated carbon is returned to the adsorber, while the mixture of steam and desorbed benzene vapors is condensed. The condensate separates into an organic and an aqueous phase and the two phases are separated by decantation. Due to the low solubility of benzene in water, most of the benzene will be concentrated in the organic phase, while the aqueous phase will contain only traces of benzene.
(a) Calculate the minimum steam flow rate required.
(b) For a steam flow rate $50 \%$ above the minimum, calculate the benzene concentration in the gas mixture leaving the desorber, and the number of ideal stages required.
The equilibrium adsorption of benzene on this activated carbon at the temperature of $380 \mathrm{~K}$ is reported as follows:
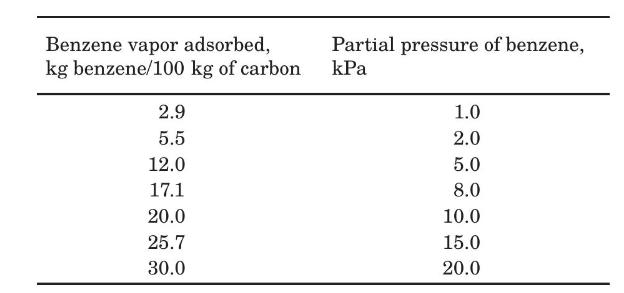
Data From Problem 3.17:-
Activated carbon is used to recover benzene from a nitrogen-benzene vapor mixture. The mixture, at $306 \mathrm{~K}$ and $1 \mathrm{~atm}$ containing $1.0 \%$ benzene by volume, is to be passed countercurrently at the rate of $1.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3} / \mathrm{s}$ to a moving stream of activated carbon so as to remove $85 \%$ of the benzene from the gas in a continuous process. The entering activated carbon contains $15 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}$ of benzene vapor (at STP) adsorbed per gram of the carbon. The temperature and total pressure are maintained at $306 \mathrm{~K}$ and $1 \mathrm{~atm}$. Nitrogen is not adsorbed.
(a) Plot the equilibrium data given in the table below as $X^{\prime}=\mathrm{kg}$ benzene/kg dry carbon, $Y^{\prime}=\mathrm{kg}$ benzene/kg nitrogen for a total pressure of $1 \mathrm{~atm}$.
(b) Calculate the minimum flow rate required of the entering carbon (remember that the entering carbon contains some adsorbed benzene).
(c) If the carbon flow is $20 \%$ above the minimum, what will be the concentration of benzene adsorbed on the carbon leaving the process?
(d) For the conditions of part (c), calculate the number of ideal stages required.
The equilibrium adsorption of benzene on this activated carbon at the temperature of $306 \mathrm{~K}$ is reported as follows:
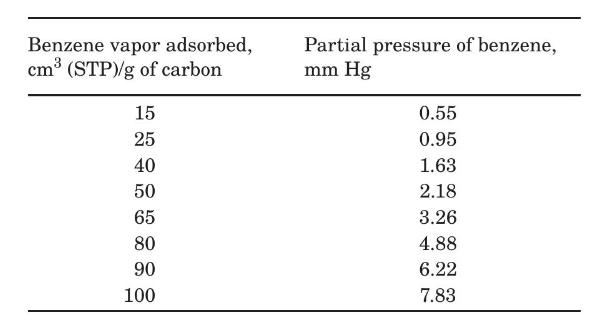
Step by Step Answer:





