The composite wall of an oven consists of three materials, two of which are of known thermal
Question:
The composite wall of an oven consists of three materials, two of which are of known thermal conductivity, \(k_{\mathrm{A}}=25 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K}\) and \(k_{\mathrm{C}}=60 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K}\), and known thickness, \(L_{\mathrm{A}}=0.40 \mathrm{~m}\) and \(L_{\mathrm{C}}=0.20 \mathrm{~m}\). The third material, \(\mathrm{B}\), which is sandwiched between materials \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{C}\), is of known thickness, \(L_{\mathrm{B}}=0.20 \mathrm{~m}\), but unknown thermal conductivity \(k_{\mathrm{B}}\).
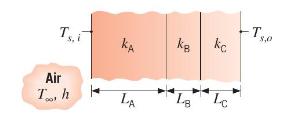
Under steady-state operating conditions, measurements reveal an outer surface temperature of \(T_{s, o}=20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), an inner surface temperature of \(T_{s, i}=600^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), and an oven air temperature of \(T_{\infty}=800^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The inside convection coefficient \(h\) is known to be \(25 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} \cdot \mathrm{K}\). What is the value of \(k_{\mathrm{B}}\) ?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119220442
8th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine





