Question: In a crank-slider setup, it is desired to maintain a constant rotational speed for driving the crank. Therefore, a flywheel was added to increase the
In a crank-slider setup, it is desired to maintain a constant rotational speed for driving the crank. Therefore, a flywheel was added to increase the spindle inertia and reduce the speed sensitivity to the driven load. See Fig. P3.9. If the
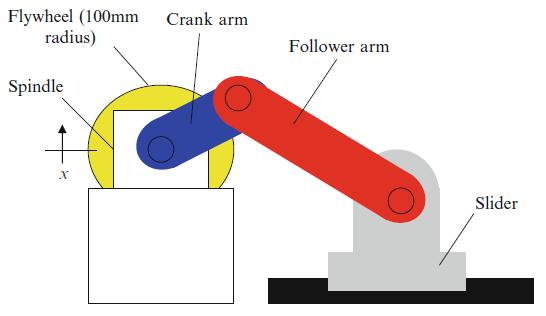
Fig. P3.9 Crank-slider with flywheel
spindle rotating speed is \(120 \mathrm{rpm}\), determine the maximum allowable eccentricity-mass product, \(m e\) (in \(\mathrm{kg}-\mathrm{m}\) ), for the flywheel if the spindle vibration magnitude is to be less than \(25 \mu \mathrm{m}\). The total spindle/flywheel mass is \(10 \mathrm{~kg}\), the effective spring stiffness (for the spindle and its support) is \(1 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{m}\), and the corresponding damping ratio is \(0.05(5 \%)\).
Given your me result, comment on the accuracy requirements for the flywheel manufacture (you may assume no rotating unbalance in the spindle).
Flywheel (100mm Crank arm radius) Spindle X Follower arm Slider
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


