1. A 4-day workweek ensures that employees will have one more day that need not be spent...
Question:
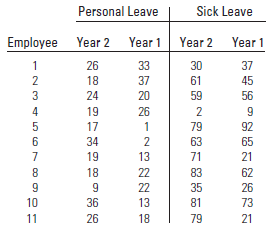
1. A 4-day workweek ensures that employees will have one more day that need not be spent at work. One possible result is a reduction in the average number of personal- leave days taken by employees on a 4-day work schedule. Do the data indicate that this is the case? Use the p-value approach to testing to reach your conclusion.
2. A 4-day workweek schedule might also have an effect on the average number of sick-leave days an employee takes. Should a directional alternative be used in this case? Why or why not?
3. Construct a 95% confidence interval to estimate the average difference in days taken for sick leave between these 2 years. What do you conclude about the difference between the average number of sick-leave days for these two work schedules?
4. Based on the analysis of these two variables, what can you conclude about the advantages of a 4-day workweek schedule?
Will a flexible workweek schedule result in positive benefits for both employer and employee? Is a more rested employee, who spends less time commuting to and from work, likely to be more efficient and take less time off for sick leave and personal leave? A report on the benefits of flexible work schedules that appeared in Environmental Health looked at the records of n = 11 employees who worked in a satellite office in a county health department in Illinois under a 4-day workweek schedule.19 Employees worked a conventional workweek in year 1 and a 4-day workweek in year 2. Some statistics for these employees are shown in the following table:
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Probability And Statistics
ISBN: 9780495389538
13th Edition
Authors: William Mendenhall, Robert J. Beaver, Barbara M. Beaver






