A pure-component pressure p i for species i in a gas mixture may be defined as the
Question:
A pure-component pressure pi for species i in a gas mixture may be defined as the pressure that species i would exert if it alone occupied the mixture volume. Thus,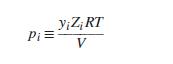 where yi is the mole fraction of species i in the gas mixture, Zi is evaluated at pi and T, and V is the molar volume of the gas mixture. Note that pi as defined here is not a partial pressure yiP, except for an ideal gas. Dalton’s “law” of additive pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the purecomponent pressures of its constituent species: P = Σipi . Show that Dalton’s “law” implies that Z = ΣiyiZi , where Zi is the compressibility factor of pure species i evaluated at the mixture temperature but at its pure-component pressure.
where yi is the mole fraction of species i in the gas mixture, Zi is evaluated at pi and T, and V is the molar volume of the gas mixture. Note that pi as defined here is not a partial pressure yiP, except for an ideal gas. Dalton’s “law” of additive pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the purecomponent pressures of its constituent species: P = Σipi . Show that Dalton’s “law” implies that Z = ΣiyiZi , where Zi is the compressibility factor of pure species i evaluated at the mixture temperature but at its pure-component pressure.
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781259696527
8th Edition
Authors: J.M. Smith, Hendrick Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart





