Question: Two special models of liquid-solution behavior are the regular solution, for which S E = 0 everywhere, and the a thermal solution, for which H
Two special models of liquid-solution behavior are the regular solution, for which SE = 0 everywhere, and the a thermal solution, for which HE = 0 everywhere.
(a) Ignoring the P-dependence of GE, show that for a regular solution,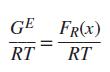 (b) Ignoring the P-dependence of GE, show that for an athermal solution,
(b) Ignoring the P-dependence of GE, show that for an athermal solution,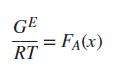 (c) Suppose that GE∕RT is described by the symmetrical equation
(c) Suppose that GE∕RT is described by the symmetrical equation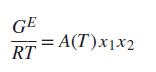 From parts (a) and (b), we conclude that where α and β are constants.
From parts (a) and (b), we conclude that where α and β are constants. 
What are the implications of Eqs. (A) and (B) with respect to the shapes of predicted solubility diagrams for LLE? Find from Eq. (A) an expression for the consolute temperature, and show that it must be an upper consolute temperature.
Suggestion: See Ex. 15.3 for numerical guidance.
Example 15.3
The simplest expression for GE ∕RT capable of predicting LLE is:

Derive the equations resulting from application of this equation to LLE.
GE FR(X) RT RT
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To tackle this problem lets first understand the different cases a Regular Solution For a regular so... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


