A mass fl ow controller (MFC) is used to accurately control the molar fl ow rate of
Question:
A mass fl ow controller (MFC) is used to accurately control the molar fl ow rate of gases into a system. A schematic of an MFC is shown below. It consists of a main tube and a sensor tube, to which a constant fraction of the fl owing gas is diverted. In the sensor tube, a constant amount of heat is provided to the heating coil. The temperature difference is measured by upstream and downstream temperature sensors, as shown. A control valve can then be opened or closed to ensure the desired fl ow rate.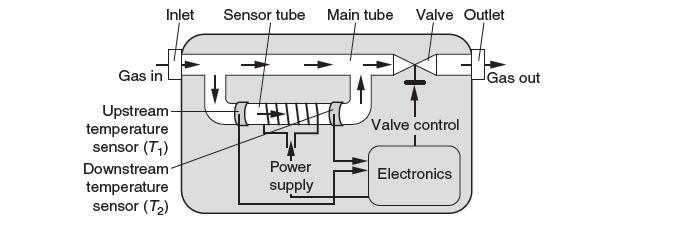
(a) Flow rates are typically reported as standard cubic centimeters per minute (SCCM), which represents the volume the gas would have at a “standard” pressure of 1.0135 bar and a “standard”
temperature of 0ºC. What molar fl ow rate (in [mol/s]), does 1 SCCM correspond to?
(b) Consider controlling the fl ow of N2. Develop an equation for the molar fl ow rate of N2 in SCCM in terms of the measured temperature difference, the heat input to the heating coil, and the fraction of gas diverted to the sensor tube. State the assumptions that you make.
(c) Instead of recalibrating the MFC for any gas that is used, conversion factors allow you to correct the MFC readout for different gases. Consider controlling SiH4 instead of N2. What conversion factor must be applied?
Step by Step Answer:






