Consider the reaction: 2 NO(g) + 2H 2 (g) N 2 (g) + 2 H 2
Question:
Consider the reaction: 2 NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Initial concentrations and rates for this reaction are given in the table below.
![Experiment 1 1234 2 4 Initial concentration (mol/L) [NO] 0.0060 0.0060 0.0010 0.0020 [H] 0.0010 0.0020 0.0060](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1701/8/6/2/85765705dc91f16c1701862855380.jpg)
(a) From the data given, determine the order for each of the reactants, NO and H2, show your reasoning, and write the overall rate law for the reaction.
(b) Calculate the value of the rate constant, k, for the reaction. Include units.
(c) For experiment 2, calculate the concentration of NO remaining when exactly one-half of the original amount of H2 has been consumed.
(d) The following sequence of elementary steps is a proposed mechanism for the reaction.
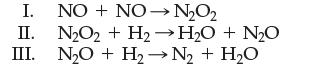
Based on the data present, explain why the first step cannot be the rate determining step.
Step by Step Answer:

Introductory Chemistry Atoms First
ISBN: 9780321927118
5th Edition
Authors: Steve Russo And Michael Silver





