Professor Ray C. Fair's voting model was introduced in Exercise 2.23. He builds models that explain and
Question:
Professor Ray C. Fair's voting model was introduced in Exercise 2.23. He builds models that explain and predict the U.S. presidential elections. See his website at http://fairmodel.econ.yale.edu/vote2016/ index2.htm and see in particular his paper entitled "Presidential and Congressional Vote-Share Equations: November 2014 Update." The basic premise of the model is that the Democratic party's share of the two-party [Democratic and Republican] popular vote is affected by a number of factors relating to the economy, and variables relating to the politics, such as how long the incumbent party has been in power, and whether the President is running for reelection. Data for 1916-2016 are in the data file fair5. The dependent variable is VOTE = percentage share of the popular vote won by the Democratic party. In addition to GROWTH and INFLAT, the explanatory variables include the following:
\(I N C U M B=1\) if there is a Democratic incumbent at the time of the election and -1 if there is a Republican incumbent.
GOODNEWS \(=\) (number of quarters in the first 15 quarters of the administration in which the growth rate of real per capita GDP is greater than \(3.2 \%\) at an annual rate except for 1920 , 1944 , and 1948, where the values are zero) \(\times I N C U M B\).
\(D P E R=1\) if the incumbent is running for election and 0 otherwise.
\(D U R=0\) if the Democratic party has been in power for one term, \(1[-1]\) if the Democratic [Republican] party has been in power for two consecutive terms, \(1.25[-1.25]\) if the Democratic [Republican] party has been in power for three consecutive terms, 1.50 for four consecutive terms, and so on.
\(W A R=1\) for the elections of 1920,1944, and 1948 and 0 otherwise.
a. Consider the regression model
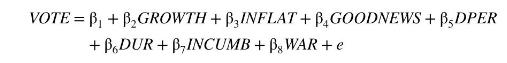
Discuss the anticipated effects of the dummy variable DPER.
b. The variable \(I N C U M B\) is somewhat different than dummy variables we have considered. Write out the regression function \(E(V O T E)\) when there is a Democratic incumbent. Write out the regression function \(E(V O T E)\) when there is a Republican incumbent. Recall that the signs of GOODNEWS, GROWTH, and INFLAT depend on INCUMB. Discuss the effects of this specification.
c. Use the data for the period 1916-2012 to estimate the proposed model. Discuss the estimation results. Are the signs as expected? Are the estimates statistically significant? How well does the model fit the data?
d. Use the regression result from part (c) to predict the value of VOTE for the 2016 election using the actual values of the explanatory variables.
e. Use the regression result from part (c) to construct a \(95 \%\) prediction interval for the value of VOTE for the 2016 election using the actual values of the explanatory variables.
f. Use the data for the period 1916-2012 to estimate the proposed model. In election year 2016, \(I N C U M B=1, D P E R=0, D U R=1\), and \(W A R=0\). Using \(G R O W T H=2.16, I N F L A T=1.37\), and GOODNEWS = 3, predict the vote in favor of the Democratic party candidate in 2016.
g. Using the results in (f), predict the vote in favor of the Democratic party in 2016 if GOODNEWS \(=3, G R O W T H=2.16\), and \(I N F L A T=0\).
h. Using the results in (f), predict the vote in favor of the Democratic party in 2016 if GOODNEWS \(=3, G R O W T H=4.0\), and \(I N F L A T=0\).
Data From Exercise 2.23:-
Professor Ray C. Fair has for a number of years built and updated models that explain and predict the U.S. presidential elections. Visit his website at https://fairmodel.econ.yale.edu/vote2016/index2.htm. See in particular his paper entitled "Presidential and Congressional Vote-Share Equations: November 2010 Update." The basic premise of the model is that the Democratic Party's share of the two-party [Democratic and Republican] popular vote is affected by a number of factors relating to the economy, and variables relating to the politics, such as how long the incumbent party has been in power, and whether the President is running for reelection. Fair's data, 26 observations for the election years from 1916 to 2016, are in the data file fair5. The dependent variable is VOTE = percentage share of the popular vote won by the Democratic Party. Consider the effect of economic growth on VOTE. If Democrats are the incumbent party \((I N C U M B=1)\) then economic growth, the growth rate in real per capita GDP in the first three quarters of the election year (annual rate), should enhance their chances of winning. On the other hand, if the Republicans are the incumbent party (INCUMB \(=-1\) ), growth will diminish the Democrats' chances of winning. Consequently, we define the explanatory variable \(G R O W T H=I N C U M B \times\) growth rate.
a. Using the data for 1916-2012, plot a scatter diagram of VOTE against GROWTH. Does there appear to be a positive association?
b. Estimate the regression VOTE \(=\beta_{1}+\beta_{2} G R O W T H+e\) by least squares using the data from 1916 to 2012. Report and discuss the estimation result. Plot the fitted line on the scatter diagram from (a).
c. Using the model estimated in (b), predict the 2016 value of VOTE based on the actual 2016 value for GROWTH. How does the predicted vote for 2016 compare to the actual result?
d. Economy wide inflation may spell doom for the incumbent party in an election. The variable \(I N F L A T=I N C U M B \times\) inflation rate, where the inflation rate is the growth in prices over the first 15 quarters of an administration. Using the data from 1916 to 2012, plot VOTE against INFLAT.
e. Using the data from 1916 to 2012 , report and discuss the estimation results for the model VOTE \(=\) \(\alpha_{1}+\alpha_{2}\) INFLAT \(+e\)
f. Using the model estimated in (e), predict the 2016 value of VOTE based on the actual 2012 value for INFLAT. How does the predicted vote for 2016 compare to the actual result?
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Econometrics
ISBN: 9781118452271
5th Edition
Authors: R Carter Hill, William E Griffiths, Guay C Lim




