Question: A is an m x n matrix with a singular value decomposition A = UV T , where U is an m x m orthogonal
A is an m x n matrix with a singular value decomposition A = UΣVT, where U is an m x m orthogonal matrix, Σ is an m x n "diagonal" matrix with r positive entries and no negative entries, and V is an n x n orthogonal matrix. Justify each answer.
Justify the statement in Example 2 that the second singular value of a matrix A is the maximum of ΙΙAxΙΙ as x varies over all unit vectors orthogonal to v1, with v1 a right singular vector corresponding to the first singular value of A.
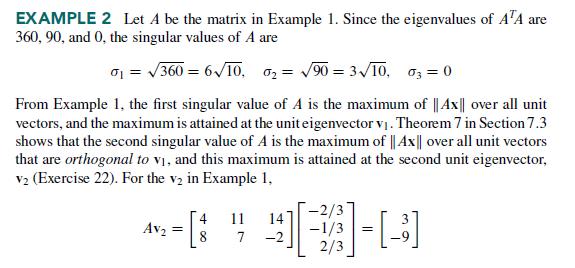
EXAMPLE 2 Let A be the matrix in Example 1. Since the eigenvalues of ATA are 360, 90, and 0, the singular values of A are 0 = 360 = 610, = 90=310, 03=0 From Example 1, the first singular value of A is the maximum of || Ax|| over all unit vectors, and the maximum is attained at the unit eigenvector v. Theorem 7 in Section 7.3 shows that the second singular value of A is the maximum of || Ax|| over all unit vectors that are orthogonal to v, and this maximum is attained at the second unit eigenvector, V2 (Exercise 22). For the v in Example 1, 4 Av = - [ 11 14 -2 -2/3 -1/3=[-
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To justify the statement in Example 2 regarding the second singular value of a matrix A we need to show that it is the maximum of Ax as x varies over ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


