P3.32 Cost behaviour patterns in a variety of settings LO 3.5 For each of the following cost
Question:
P3.32 Cost behaviour patterns in a variety of settings LO 3.5 For each of the following cost Items (1 to 11), choose the graph,
(a) to (I), that best represents it: 1. Cost of electricity at a university. For low student enrolments, electricity costs increase with enrolment, but at a decreasing rate. For high student enrolments, electricity costs increase at an increasing rate. 2. Charges for international telephone calls, which are based on the number of minutes per month. The charge is $0.25 per minute, up to 600 minutes. Additional minutes (above 600) are free. 3. Cost of outsourcing pathology testing by a hospital. The hospital pays an independent lab a fee of $10000 per month plus $5 for each test performed. 4. Salary costs of the shift supervisors at a courier company. Each shift is eight hours. The depot operates with one, two or three shift supervisors simultaneously, at various times of the year, depending on the volume of delivery work. 5. Cost of 24-hour security services at a factory, provided by an external security company.
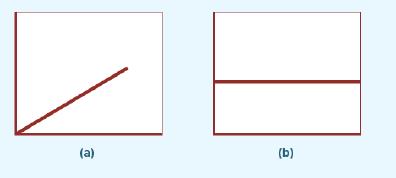
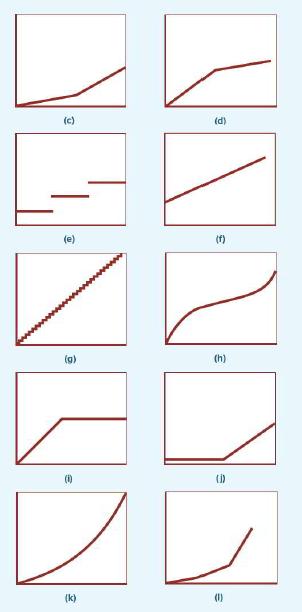
6. Wages of waiters in a restaurant. Waiters are part-time workers who are scheduled to work in three-hour blocks. 7. Cost of electricity during peak-demand periods, based on the following schedule: Up to 10000 kilowatt hours (kWh) Above 10000 kWh $0.90 per kWh $1.12 per kWh (The price schedule is designed to discourage overuse of electricity during periods of peak demand.)
8. Cost of sheet metal used to manufacture automobiles, priced by weight (per kilogram, or part thereof). 9. Cost of chartering a private aeroplane. The cost is $410 per hour for the first three hours of a flight. Then the cost drops to $305 per hour. 10. Under a licensing agreement with an Indonesian import/export company, your firm has begun shipping machine tools to several countries. The terms of the agreement call for an annual licensing fee of $100000 to be paid to the Indonesian import company if total exports are under $4.000.000. For sales in excess of $4000 000, an additional licensing fee of 7 per cent of sales is due. 11. Tariffs paid by a wine exporter. On one Pacific island, a tariff must be paid by the wine exporter for every case of wine brought into that country. The tariff schedule is the following: 0 to 6000 cases per year 6001 to 12000 cases per year Above 12000 cases per year $11 per case $14 per case $19 per case
Step by Step Answer:

Management Accounting Information For Creating And Managing Value
ISBN: 9781743767603
9th Edition
Authors: Kim Langfield Smith, David Smith, Paul Andon, Ronald W. Hilton




