Intermediate: Preparation of functional budgets D Limited is preparing its annual budgets for the year to 31
Question:
Intermediate: Preparation of functional budgets D Limited is preparing its annual budgets for the year to 31 December 2001. It manufactures and sells one product, which has a selling price of £150. The marketing director believes that the price can be increased to £160 with effect from 1 July 2001 and that at this price the sales volume for each quarter of 2001 will be as follows: Sales for each quarter of 2002 are expected to be 40 000 units.
Each unit of the finished product which is manufactured requires four units of component R and three units of component T, together with a body shell S. These items are purchased from an outside supplier. Currently prices are:
The components are expected to increase in price by 10% with effect from 1 April 2001; no change is expected in the price of the shell.
Assembly of the shell and components into the finished product requires 6 labour hours: labour is currently paid £5.00 per hour. A 4% increase in wage costs is anticipated to take effect from 1 October 2001.
Variable overhead costs are expected to be £10 per unit for the whole of 2001; fixed production overhead costs are expected to be £240 000 for the year, and are absorbed on a per unit basis. Stocks on 31 December 2000 are expected to be as follows: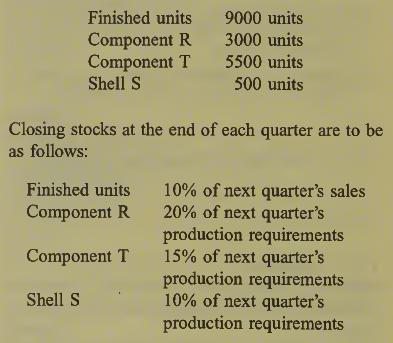
Requirement:
(a) Prepare the following budgets of D Limited for the year ending 31 December 2001, show¬ ing values for each quarter and the year in total:
(i) sales budget (in £s and units)
(ii) production budget (in units)
(iii) material usage budget (in units)
(iv) production cost budget (in £s).
(b) Sales are often considered to be the principal budget factor of an organisation.
Requirement:
Explain the meaning of the ‘principal budget factor’ and, assuming that it is sales, explain how sales may be forecast making appropriate reference to the use of statistical techniques and the use of microcomputers.
Step by Step Answer:






