Easy Learning (EL) develops on line learning platforms for companies using gamification techniques to make the learning
Question:
Easy Learning (EL) develops on line learning platforms for companies using gamification techniques to make the learning experience engaging. Research shows that employees are far more likely to use learning platforms if they are easy and fun to use. EL's approach is to embed the learning content, usually a series of multiple choice questions, in the games they use in their platform. EL works with company management to develop the learning content and their platforms have been used in a wide variety of functional areas such a~ manufacturing, sales, customer service, distribution, and product development. EL has developed a strong reputation for being the most creative and reliable developer of on line learning platforms and the company ha~ clients across Canada and the United States.
Competition has increased considerably over the past five years, with several start-up companies offering their own versions of on line learning platforms. Given this, EL is placing increased emphasis on its customer acquisition activities, which range from attending tech conventions, developing webinars presenting their research at conferences, follow-up meetings and calls with prospective customers, and on line advertising. Annual recurring revenue (ARR) for use of the learning platform from each customer averages $100,000, so acquiring and retaining customers is critical to EL's success.
For the next fiscal period, Claire Jackson, EL's CEO and founder, has told die senior management team that she wants to acquire 40 new customers compared to the 20 new customers that were acquired in the fiscal period just ended. Jackson believes that it is reasonable to expect the marketing department to spend in total the equivalent of about one year's ARR that will be generated by the number of new customers acquired in that year.
The total number of monthly follow-up activities with prospective client~ (e.g., calls, meetings, product demos, etc.) and the total marketing department costs for last year are shown below:
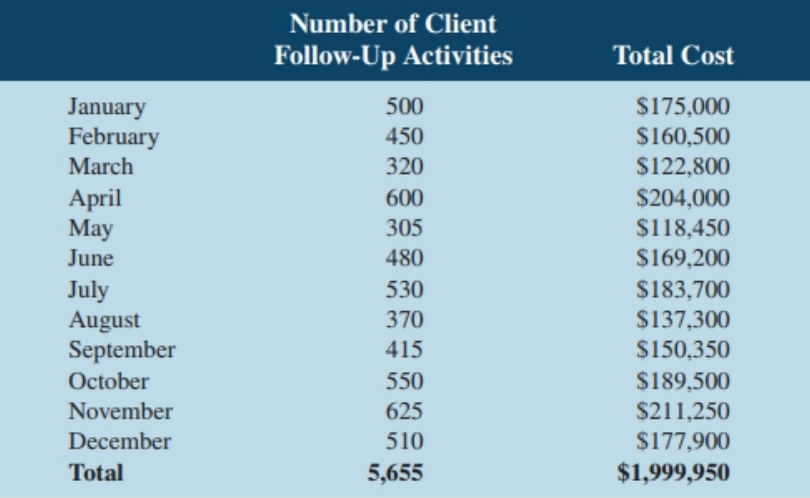
Required:
1. Assuming no change to the cost behaviour implied by the data from last year and no increase in costs due to inflation or other factors, estimate die total spending that will be required by the marketing department to acquire 40 new customers next year. You can further assume that the relation-ship between the number of follow-up activities with prospective clients and the number of new customers actually acquired next year, the conversion ratio, will be the same as it was last year (i.e., 20/5,655, or 0.35%).
2. Given your answer to part (I), is Jackson likely to approve the estimated total spending by the marketing department next year? Show your calculations.
3. The vice-president of marketing estimates that the conversion ratio can be improved to 0.40% by paying a $10,000 bonus to employees for "converting" a customer and by increasing the amount spent on follow-up activities with prospective customers to $350 per activity. Is Jackson likely to approve these estimated increases? Show your calculations.
4. Given the increase in costs described in part (3) above, what would the new conversion ratio need to be in order for Jackson to be indifferent between making the suggested changes and doing nothing? Show your calculations.
Step by Step Answer:

Managerial Accounting
ISBN: 9781259275814
11th Canadian Edition
Authors: Ray H Garrison, Alan Webb, Theresa Libby





