Sharpton Fabricators Corporation manufactures a variety of parts for the automotive industry. The company uses a job-order
Question:
Sharpton Fabricators Corporation manufactures a variety of parts for the automotive industry. The company uses a job-order costing system with a plant wide predetermined overhead rate based on direct labour hours. On December JO, 2015, the company's controller made a preliminary estimate of the predetermined overhead rate for 2016. The new rate was based on the estimated total manufacturing overhead cost of $3,402,000 and die estimated 63,000 total direct labour-hours for 2016:
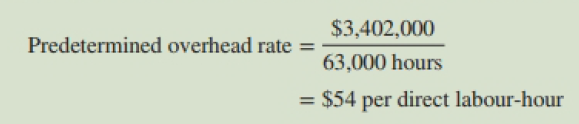
This new predetermined overhead rate was communicated to top managers in a meeting on December 11. The rate did not cause any comment because it was within a few cents of the overhead rate that had been used during 2015. One of the subjects discussed at the meeting was a proposal by the production manager to purchase an automated milling machine centre built by Central Robotics. The president of Sharpton Fabricators, Kevin Reynolds, agreed to meet with the regional sales representative from Central Robotics to discuss the proposal.
On the day following the meeting, Reynolds met with Jay Warner, Central Robotics' sales representative. The following discussion took place:
Reynolds: Lisa Winter, our production manager, asked me to meet with you since she's interested in installing an automated milling machine centre. Frankly, I'm skeptical. You're going to have to show me this isn't just another expensive toy for Lisa's people to play with.
Warner: That shouldn't be too difficult, Kevin. The automated milling machine centre has three major advantages. First, it's much faster than the manual methods you're using. It can process about twice as many parts per hour as your current ,milling machines. Second, it's much more flexible. There are some up-front programming costs, but once those have been incurred, almost no setup is required on the machines for standard operations. You just punch in the code of the standard operation, load the machine's hopper with raw material, and the machine does the rest.
Reynolds: Yeah, but what about cost? Having twice the capacity in the milling machine area won't do us much good. That centre is idle much of the time, anyway.
Warner: I was getting there. The third advantage of the automated milling machine centre is lower cost. Winters and I looked over your present operations, and we estimated that the automated equipment would eliminate the need for about 6,000 direct labour-hours a year. What is your direct labour cost per hour?
Reynolds: The wage rate in the milling area averages about $32 per hour. Fringe benefits raise that figure to about $41 per hour.
Warner: Don't forget your overhead.
Reynolds: Next year the overhead rate will be about $54 per direct labour-hour.
Warner: So including fringe benefits and overhead, the cost per direct labour-hour is about $95.
Reynolds: That's right.
Warner: Since you can save 6,000 direct labour-hours per year, the cost savings would amount to about $570,000 a year, and our 60-month lease plan would require payments of only $348,000 per year.
Reynolds: Sold ! When can you install the equipment?
Shortly after this meeting, Reynolds informed the company's controller of the decision to lease the new equipment, which would be installed over the Christmas vacation period. The controller realized that this decision would require a recomputation of the predetermined overhead rate for 2016, since the decision would affect both the manufacturing overhead and the direct labour-hours for the year. After talking with both the production manager and the sales representative from Central Robotics, the controller discovered that in addition to the annual lease cost of $348,000, the new machine would also require a s killed technician/programmer who would have to be hired at a cost of $50,000 per year to maintain and program the equipment. Both of these costs would be included in factory overhead. There would be no other changes in total manufacturing overhead cost, which is almost entirely fixed . The controller assumed that the new machine would result in a reduction of 6,000 direct labour-hours for the year from the levels that had initially been planned.
When the revised predetermined overhead rate for 2016 was circulated among the company's top managers, there was considerable dismay.
Required:
1. Recompute the predetermined rate assuming that the new machine will be installed. Explain why the new predetermined overhead rate is higher (or lower) than the rate that was originally estimated for 2016.
2. What effect (if any) would this new rate have on the cost of jobs that do not use the new automated milling machine?
3. Why would managers be concerned about the new overhead rate?
4. After seeing the new predetermined overhead rate, the production manager admitted that he probably wouldn't be able to eliminate all of the 6,000 direct labour-hours. He had been hoping to accomplish the reduction by not replacing workers who retire or quit, but that would not be possible. As a result, the real labour savings would only be about 2,000 hours-one worker. In the light of this additional in formation, evaluate the original decision to acquire the automated milling machine from Central Robotics.
CorporationA Corporation is a legal form of business that is separate from its owner. In other words, a corporation is a business or organization formed by a group of people, and its right and liabilities separate from those of the individuals involved. It may...
Step by Step Answer:

Managerial Accounting
ISBN: 9781259275814
11th Canadian Edition
Authors: Ray H Garrison, Alan Webb, Theresa Libby





