The BouguerBeer law (sometimes called the LambertBeer law or Beers law) states that A = alc, where
Question:
The Bouguer–Beer law (sometimes called the Lambert–Beer law or Beer’s law) states that A = alc, where A is the of a solution, defined as log10 (I0/I ), where I0 is the incident intensity of light at the appropriate wavelength and I is the transmitted intensity; l is the length of the cell through which the light passes; and c is the concentration of the absorbing substance. The coefficient a is called the molar absorptivity if the concentration is measured in moles per liter. The following is a set of data for the absorbance of a set of solutions of disodium fumarate at a wavelength of 250 nm.
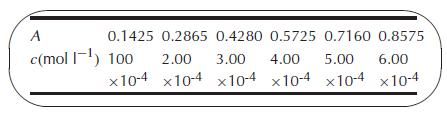
Using a linear least-squares fit with intercept set equal to zero, find the value of the absorptivity a if l = 1.000 cm. For comparison, carry out the fit without specifying zero intercept.
Step by Step Answer:






