In a static firing test, a rocket is anchored to a rigid wall by a spring-damper system,
Question:
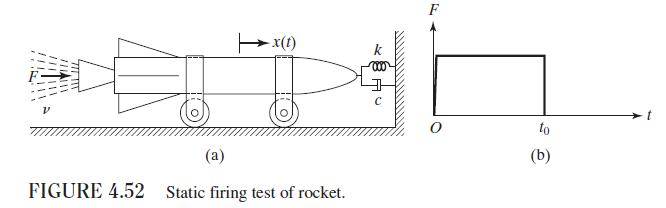
In a static firing test, a rocket is anchored to a rigid wall by a spring-damper system, as shown in Fig. 4.52(a). The thrust acting on the rocket reaches its maximum value \(F\) in a negligibly short time and remains constant until the burnout time \(t_{0}\), as indicated in Fig. 4.52(b). The thrust acting on the rocket is given by \(F=m_{0} v\), where \(m_{0}\) is the constant rate at which fuel is burnt and \(v\) is the velocity of the jet stream. The initial mass of the rocket is \(M\), so that its mass at any time \(t\) is given by \(m=M-m_{0} t, 0 \leq t \leq t_{0}\). If the data are \(k=7.5 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{m}\), \(c=0.1 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~N}-\mathrm{s} / \mathrm{m}, m_{0}=10 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{s}, v=2000 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}, M=2000 \mathrm{~kg}\), and \(t_{0}=100 \mathrm{~s}\), (1) derive the equation of motion of the rocket, and (2) find the maximum steady-state displacement of the rocket by assuming an average (constant) mass of \(\left(M-\frac{1}{2} m_{0} t_{0}\right)\).
Step by Step Answer:






