A body of mass (m=10.0 mathrm{~g}) is dropped from an initial height (h=50.0 mathrm{~cm}) along a frictionless
Question:
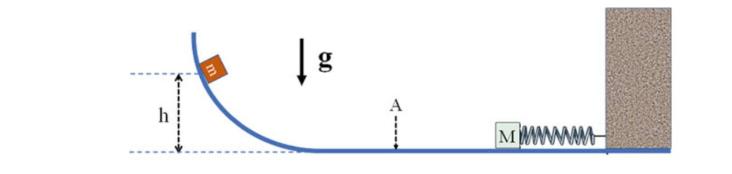
A body of mass \(m=10.0 \mathrm{~g}\) is dropped from an initial height \(h=50.0 \mathrm{~cm}\) along a frictionless circular guide, as in Fig. 8.15. At the end of the circular guide, the body moves on a horizontal plane also without friction and hits into a bumper of mass \(M\), initially stationary, connected to a spring of negligible mass and elastic constant \(k=3.40 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{m}\). The other end of the spring is attached to a wall. Assuming that the collision is central and elastic and knowing that, after the collision, the body of mass \(m\) goes up the rail to the height \(h_{f}=10.0 \mathrm{~cm}\) calculate:
1. the velocity of mass \(m\) when it is at point \(\mathrm{A}\), before and after the impact;
2. the mass \(M\) of the bumper; and 3. the velocity of the bumper after the impact;
4. the amplitude \(A_{o}\) of the oscillations of the bumper after the impact, neglecting friction.
Fig. 8.15
Step by Step Answer:






