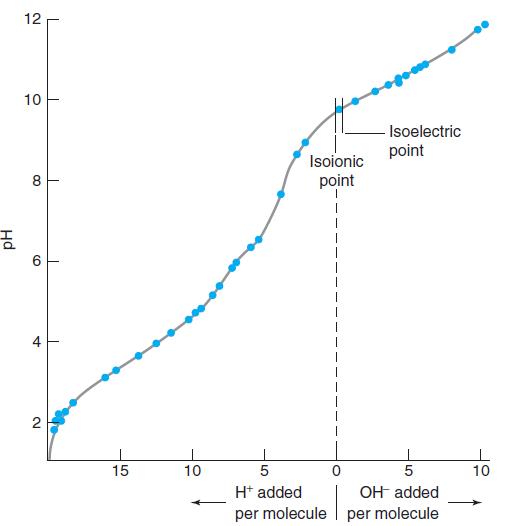
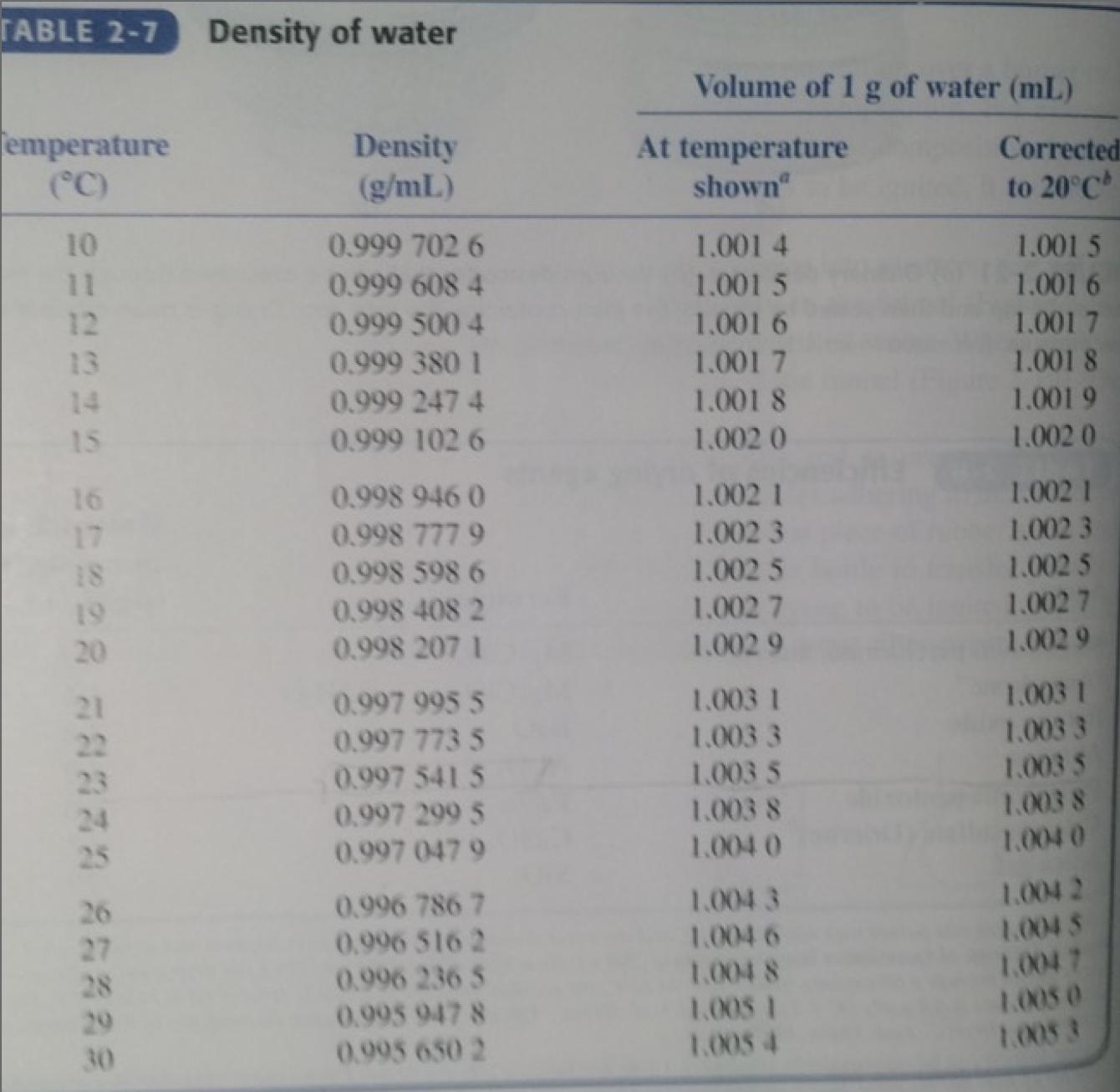
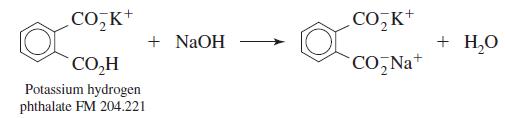
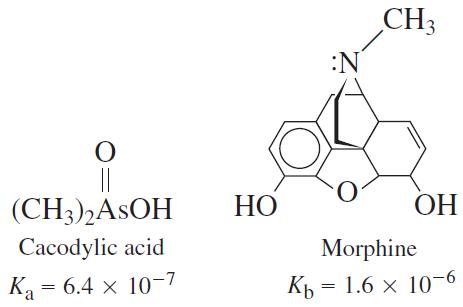
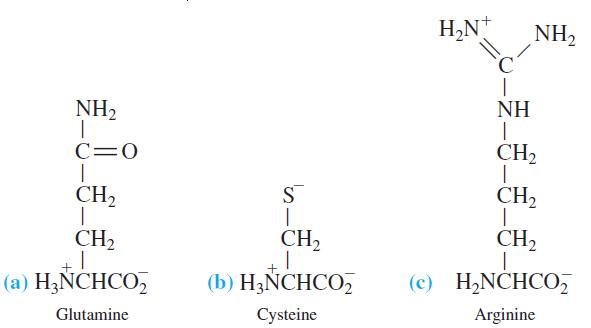
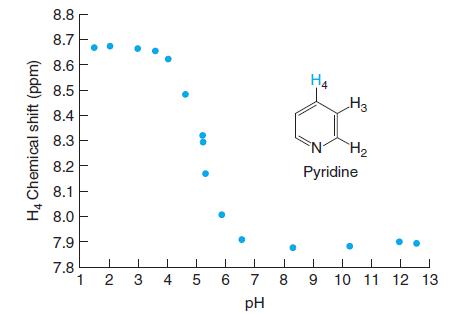
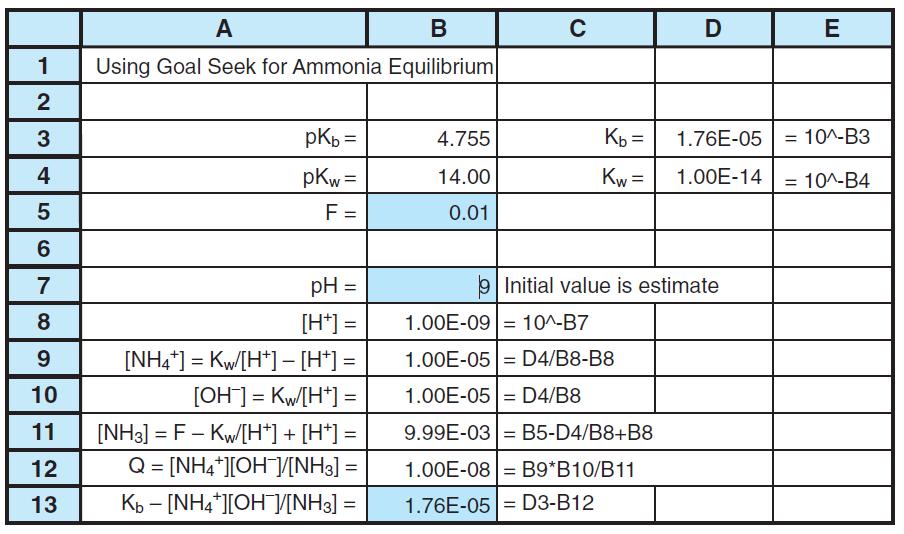
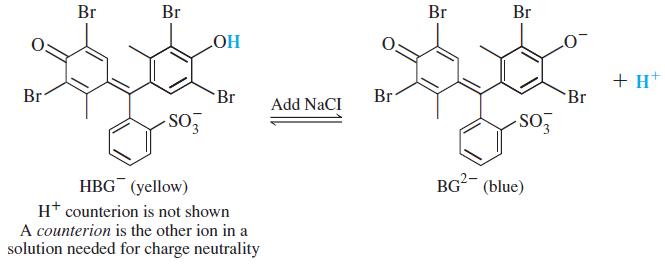
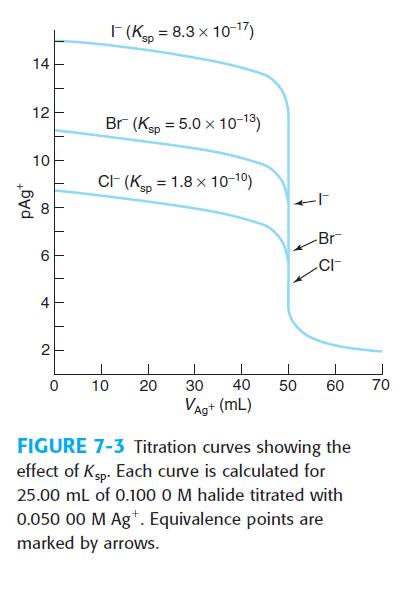
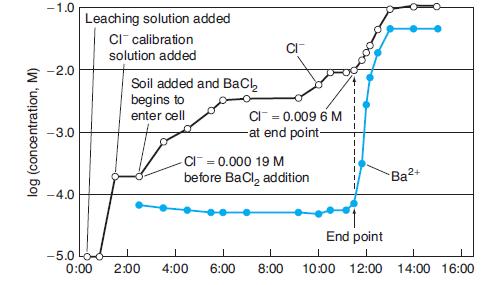
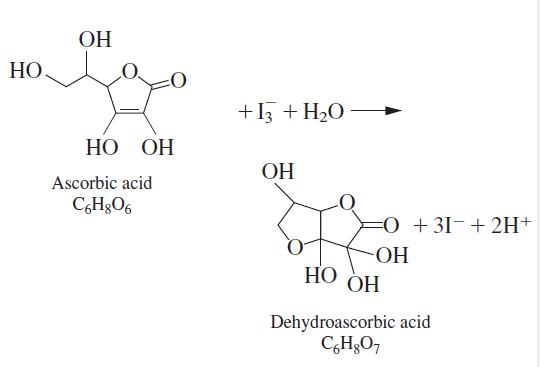
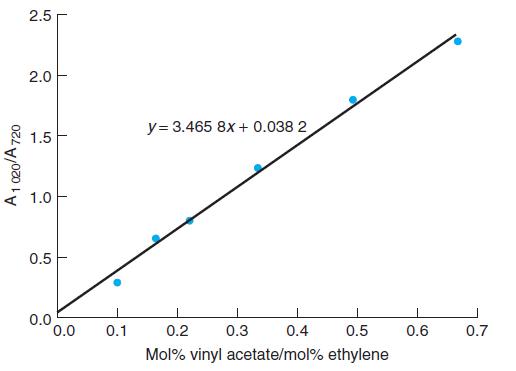
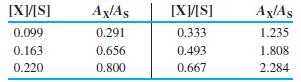
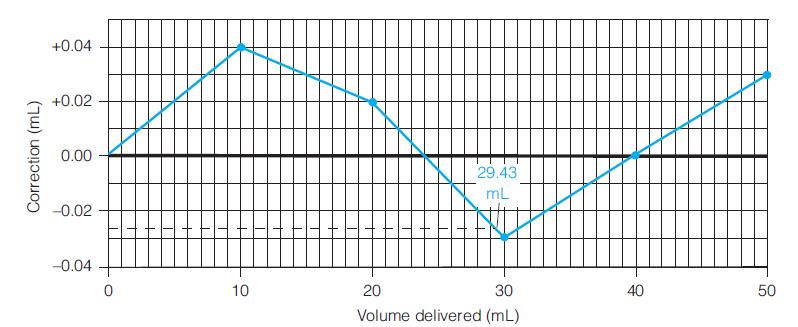
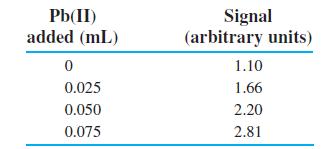
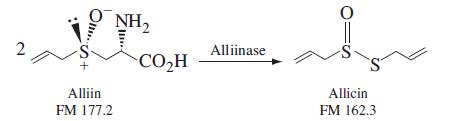
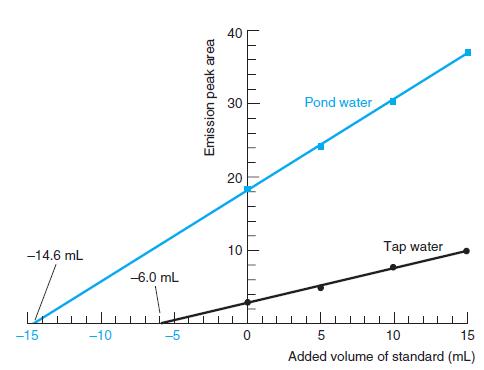
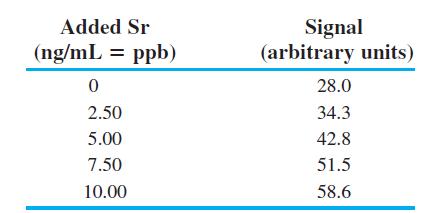
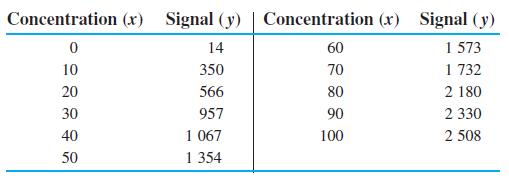
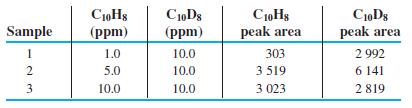
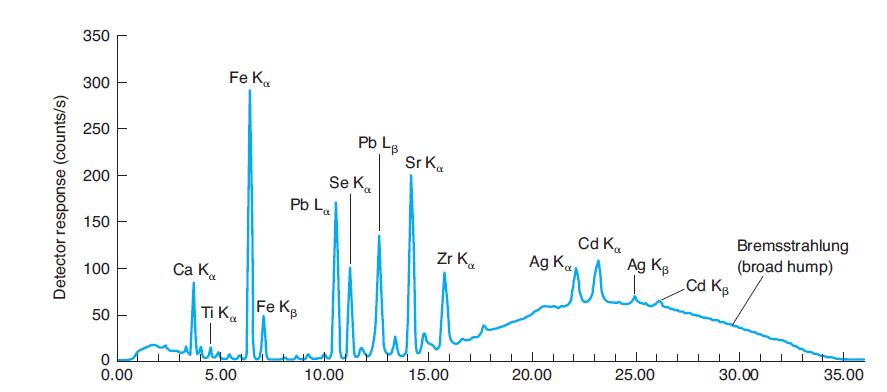
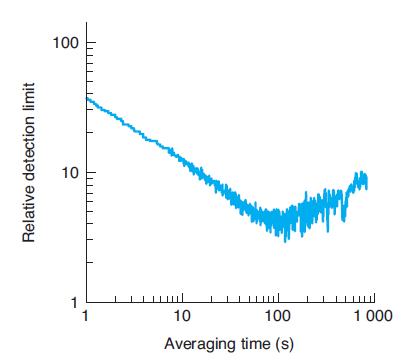
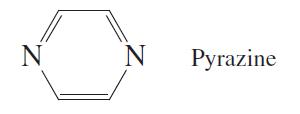
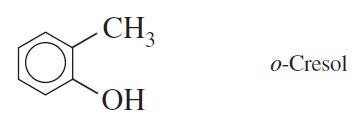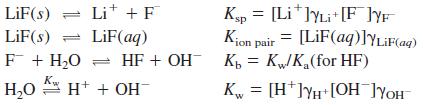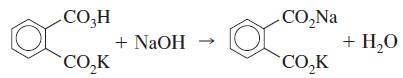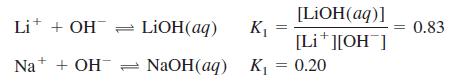Quantitative Chemical Analysis 9th Edition Daniel C. Harris - Solutions
Discover the ultimate resource for mastering "Quantitative Chemical Analysis 9th Edition" by Daniel C. Harris with our comprehensive solution manual. Access the answers key, solutions, and solved problems online to enhance your learning experience. Our platform offers free downloads of chapter solutions and a detailed test bank to aid your study sessions. Benefit from step-by-step answers and the instructor manual to gain deeper insights into textbook questions and answers. Whether you're seeking solutions in PDF format or looking for a robust guide, our expertly curated content ensures you excel in your studies.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()