Question:
Use a 50\% subsample of the fishing mode choice data of Section 15.2.
(a) Estimate the conditional logit model of Section 15.2.1.
(b) Comment on the statistical significance of parameter estimates.
(c) What is the effect of an increase in price on the various modes of fishing?


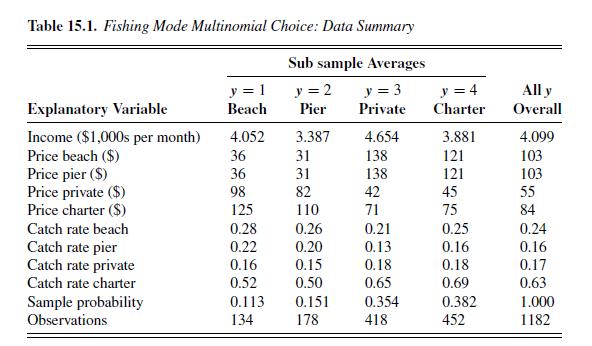
Transcribed Image Text:
15.2. Example: Choice of Fishing Mode This section illustrates multinomial logit, the simplest unordered multinomial model, and variations detailed in Section 15.4 that permit regressors to vary across alterna- tives. The emphasis is on interpretation of estimated models. The marginal effect of a change in a regressor is more complicated than the usual impact on a single condi- tional mean. For multinomial data there is instead a separate marginal effect on the probability of each outcome, and these marginal effects sum to zero since probabilities sum to one. The application is to choice of fishing mode. The dependent variable y takes value 1, 2, 3, or 4 depending on which of the four mutually exclusive alternative modes of fishing - respectively, beach, pier, private boat, and charter boat - is chosen. An unordered multinomial model such as multinomial logit is appropriate, since there is no clear ordering of the outcome variable. Regressors are individual income, which does not vary with fishing mode, and price and catch rate, which do vary by fishing mode and across individuals. The sample of 1,182 people comes from a survey conducted by Thomson and Crooke (1991) and analyzed by Herriges and Kling (1999). The data are summarized in Table 15.1, which gives averages for the subsamples of people who chose each of the modes as well as the overall sample average of regressors.










