Question: A quantum particle with charge q, mass m, and momentum p in a magnetic field B(r) = A(r) has velocity (r) = p/m
A quantum particle with charge q, mass m, and momentum p in a magnetic field B(r) = ∇ × A(r) has velocity ν(r) = p/m − (q/m)A(r). This means that a charge distribution ρ(r) generates a “diamagnetic current” j (r) = −(q/m)ρ(r)A(r) when it is placed in a magnetic field.
(a) Show that A(r) = 1/ 2 B × r is a legitimate vector potential for a uniform magnetic field B.
(b) Let ρ(r) = ρ(r) be the spherically symmetric charge distribution associated with the electrons of an atom. Expose the atom to a uniform magnetic field B and show that the ensuing diamagnetic current induces a vector potential
![Non-18+ [1 ][ = Ho eB xr Aind (r) = 4 6m](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1679/3/2/4/7336418763db9f8d1679324733323.jpg)
(c) Expand Aind(r) for small values of r and show that the diamagnetic field at the atomic nucleus can be written in terms of ϕ(0), the electrostatic potential at the nucleus produced by ρ(r):
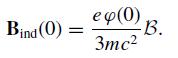
This formula was obtained by Willis Lamb in 1941. He had been asked by Isidore Rabi to determine
whether Bind(0) could be ignored when nuclear magnetic moments were extracted from molecular beam data.
Non-18+ [1 ][ = Ho eB xr Aind (r) = 4 6m dp' P(r') r'
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b c If B is a cons... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


