Mutations in .trimcric G proteins can cause many diseases in humans. Patients with acromegaly often have pituitary
Question:
a. To investigate the effect of the mutation on Gas, activity, wild-type and mutant Gas, cDNAs were transfected into cells that lack the Gas, gene. These cells express a β-radrenergic receptor, which can be activated by isoproterenol, a β2- adrenergic receptor agonist. Membranes were isolated from transfected cells and assayed for adcnylyl cyclase activity in the presence of GTP or the hydrolysis-resistant GTP analog, GTP€”γS. from the figure below, what do you conclude about the effect of the mutation on Gas, activity in the presence of GTP alone compared with GTP€”γS alone or GTP plus isoproterenol ( iso)?
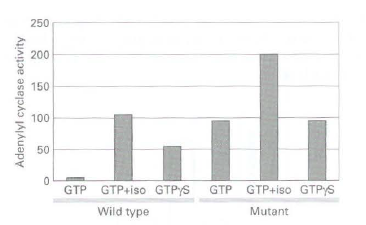
b. In the transfected cells described in part (a), what would you predict would be the cAMP levels in cells transfccted with the wild-type Gas , and the mutant Gas,? What effect might this have on the cells?
c. To further characterize the molecular defect caused by this mutation, the intrinsic GTPase activity present in both wild-type and mutant Gas, was assayed. Assays for GTPase activity showed that the mutation reduced the kcat-GTP (catalysis rate constant for GTP hydrolysis) from a wild-type value of 4.1 min-1 to the mutant value of 0.1 min-1. What do you conclude about the effect of the mutation on the GTPase activity present in the mutant G0 , subunit? How do these GTPase results explain the adenylyl cyclase results shown in part (a)?
Step by Step Answer:

Molecular Cell Biology
ISBN: 978-1429234139
7th edition
Authors: Harvey Lodish, Arnold Berk, Chris A. Kaiser, Monty Krieger, Anthony Bretscher, Hidde Ploegh, Angelika Amon, Matthew P. Scott





