A conducting bar of width (w=0.12 mathrm{~m}) and mass (m=) (8.0 mathrm{~g}) can slide freely on two
Question:
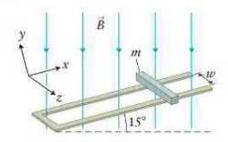
A conducting bar of width \(w=0.12 \mathrm{~m}\) and mass \(m=\) \(8.0 \mathrm{~g}\) can slide freely on two parallel conducting rails positioned at an incline of \(\theta=15^{\circ}\) (Figure P29.71). The rails are connected at their base by a piece of conducting material. The distance between the rails is \(w\), and the resistance in the rails is \(R=0.20 \mathrm{~V} / \mathrm{A}\). A uniform magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) is exactly vertical as indicated in the drawing, with \(B=0.50 \mathrm{~T}\). At what constant (terminal) speed does the bar slide down the incline? Ignore friction.
Data from Figure P29.71
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





