A filament-wound composite drive shaft for a helicopter transmits a torque (T) that generates shear loading of
Question:
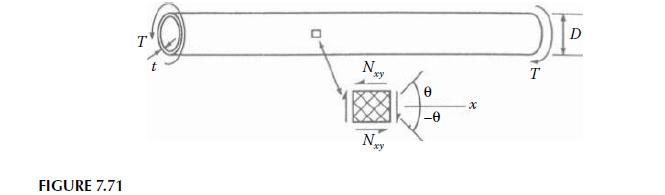
A filament-wound composite drive shaft for a helicopter transmits a torque \(T\) that generates shear loading of the shaft material, as shown in Figure 7.71. The shaft is to be designed as a hollow tube with a two-ply \([+\theta /-\theta]\) laminated wall. If the outside diameter, the length, and the material density are fixed, use invariants to determine the angle \(\theta\), which should be used to maximize the shear stiffness-to-weight ratio, \(A_{66} / \mathrm{W}\), where \(A_{66}\) is the laminate shear A filament-wound composite drive shaft for a helicopter transmits a torque \(T\) that generates shear loading of the shaft material, as shown in Figure 7.71. The shaft is to be designed as a hollow tube with a two-ply \([+\theta /-\theta]\) laminated wall. If the outside diameter, the length, and the material density are fixed, use invariants to determine the angle \(\theta\), which should be used to maximize the shear stiffness-to-weight ratio, \(A_{66} / \mathrm{W}\), where \(A_{66}\) is the laminate shear stiffness and \(W\) is the shaft weight. It may be assumed that the shaft diameter, \(D\), is much greater than the wall thickness, \(t\).
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Composite Material Mechanics
ISBN: 9781498720694
4th Edition
Authors: Ronald F. Gibson





