A thin-walled filament-wound composite pressure vessel has fibers wound at a helical angle , as shown in
Question:
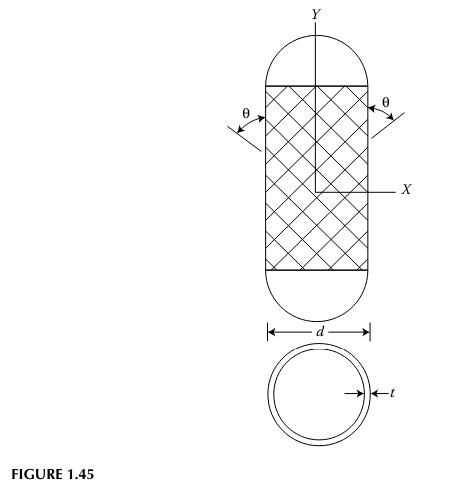
A thin-walled filament-wound composite pressure vessel has fibers wound at a helical angle θ, as shown in Figure 1.45. Ignore the resin matrix material and assume that the fibers carry the entire load. Also assume that all fibers are uniformly stressed in tension. This gross oversimplification is the basis of the so-called “netting analysis,” which is actually more appropriate for stress analysis of all-fiber textile fabrics. Using this simplified analysis, show that the angle θ must be 54.74° in order to support both the hoop (tangential) and axial stresses that are generated in a thin-walled pressure vessel. (See any mechanics of materials book for the stress analysis of a thin-walled pressure vessel.)
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Composite Material Mechanics
ISBN: 9781498720694
4th Edition
Authors: Ronald F. Gibson





