Question
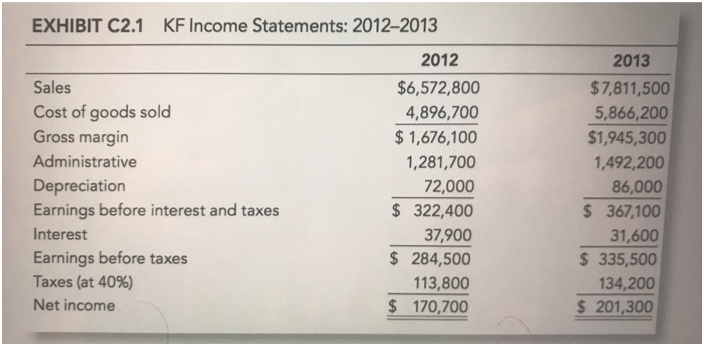
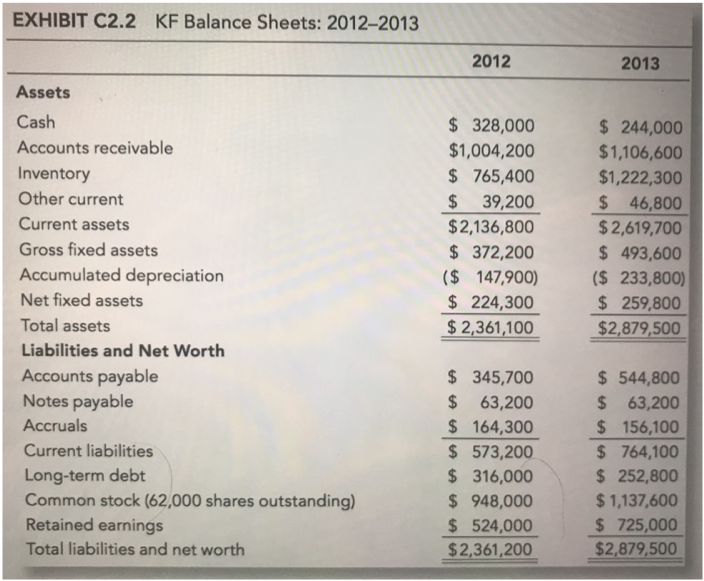
1. Using the data in Exhibits C2.1 and C2.2, calculate and analyze the firm's 2012 and 2013 ratios. 2. Part of Owen's evaluation will consist
1. Using the data in Exhibits C2.1 and C2.2, calculate and analyze the firm's 2012 and 2013 ratios.
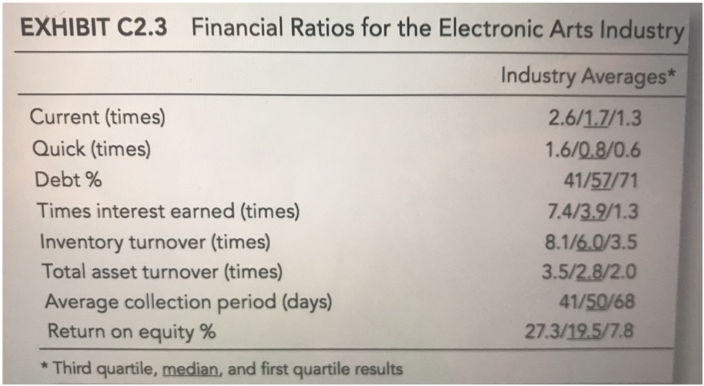
2. Part of Owen's evaluation will consist of comparing the firm's ratios to the industry as shown in Exhibit C3.3. Discuss the limitations of such a comparative financial analysis. In view of these limitations, why are such industry comparisons so frequently made? (Note: Sales are forecast to be $8.25 million in 2014.)
3. Owen thinks that the profitability of the firm has been hurt by Tessa's reluctance to use much interest-bearing debt. Is this a reasonable position? Explain.
4. The case mentions that Tessa rarely takes trade discounts, which are typically 1%/10, net 30. Does this seem like a wise financial move? Explain.
5. Is the estimate of $35 to $40 for Owen's shares a fair evaluation?
6. What do you recommend that Owen and Tessa do to improve their company?
Borrowing Issues:
Tessa's personality compels her to make virtually all major operating decisions. Owen is concerned that firms the size of KF have had difficulty maintaining a stable bank relationship. Due to increasingly strict federal regulations, some lenders have called in loans, and most are scrutinizing new business loans very carefully. Consequently, Tessa views bank debt financing as unreliable, a potential problem should business become slow, and thinks that loan officers are capable of wasting her time.
Owen isn't sure what to make of these arguments, but he is concerned that avoiding debt has significantly reduced KF's financial flexibility because it means that all projects will have to be equity financed. In fact, over the past five years there have been no dividends because all earnings have been reinvested.
And three years ago each of the partners had to contribute $20,000 of capital in order to meet the company's needs.
Another infusion of capital may be necessary since the firm's present cash position is low by historical standards. More important, however. Owen feels that the company is not benefiting from the leverage effect of debt financing and that this hurts the profitability of the firm to the two owners.
Working Capital:
Owen suspects that KF's inventory is excessive. He stated, "Capital is unnecessarily tied up in inventory." Tessa's position is that a large inventory is necessary to provide speedy delivery to customers. She replied, "Our customers expect quick service when a game is in demand, and a large inventory helps us to provide it." Owen is skeptical of this argument and wonders if there isn't a more efficient way of providing good service.
He also questions Tessa's credit standards and collection procedures, and believes that Tessa has been quite generous in granting payment extensions to customers. At one point, nearly 45 percent of the company's receivables were more than 90 days overdue. Furthermore, Tessa would continue to accept and ship orders to these resellers even when it was clear that their ability to pay was marginal. Tessa's position is that she doesn't want to lose sales and that the difficult times are only temporary.
Owen wonders about the wisdom of passing up trade discounts. Vendors frequently offer KF terms of 1%/10, net 30. That is, KF receives a 1% percent discount if a bill is paid in 10 days and in any event full payment is expected within 30 days. Tessa rarely takes these discounts because she "wants to hold onto our cash as long as possible." She also notes that "the discount isn't especially generous and 981/2 percent of the bill must still be paid."
Final Thoughts:
Despite all of Owen's concerns, however, the relationship between the two partners has been relatively smooth over the years. And he admits that he may be unduly critical of Tessa's management decisions. "After all," he concedes, "she seems to have reasons for what she does, and we have never lost money since we started, which is an impressive record, really, for a firm in our business." Owen has discussed with two advisors the possibility of selling his half of the firm. Since KF is not publicly traded, the market value of the company's stock must be estimated. The consultants believe that KF is worth between $35 and $40 per share, figures that appear reasonable to Owen.
EXHIBIT C2.1 KF Income Statements: 2012-2013 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Administrative Depreciation Earnings before interest and taxes Interest Earnings before taxes Taxes (at 40%) Net income 2012 $6,572,800 4,896,700 $1,676,100 1,281,700 72,000 $ 322,400 37,900 $ 284,500 113,800 $ 170,700 2013 $7,811,500 5,866,200 $1,945,300 1,492,200 86,000 $367,100 31,600 $335,500 134,200 $ 201,300 EXHIBIT C2.2 KF Balance Sheets: 2012-2013 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Other current Current assets Gross fixed assets Accumulated depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets Liabilities and Net Worth Accounts payable Notes payable Accruals Current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock (62,000 shares outstanding) Retained earnings Total liabilities and net worth 2012 $328,000 $1,004,200 $765,400 $ 39,200 $2,136,800 $ 372,200 ($ 147,900) $ 224,300 $2,361,100 $ 345,700 $63,200 $164,300 $ 573,200 $ 316,000 $948,000 $ 524,000 $2,361,200 2013 $ 244,000 $1,106,600 $1,222,300 $ 46,800 $2,619,700 $493,600 ($ 233,800) $ 259,800 $2,879,500 $544,800 $63,200 $ 156,100 $764,100 $ 252,800 $1,137,600 $ 725,000 $2,879,500 EXHIBIT C2.3 Financial Ratios for the Electronic Arts Industry Industry Averages* Current (times) Quick (times) Debt % Times interest earned (times) Inventory turnover (times) Total asset turnover (times) Average collection period (days) Return on equity % *Third quartile, median, and first quartile results 2.6/1.7/1.3 1.6/0.8/0.6 41/57/71 7.4/3.9/1.3 8.1/6.0/3.5 3.5/2.8/2.0 41/50/68 27.3/19.5/7.8
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Analysis of Ratio 1 Here current Ratio has remained stable in 2012 and 2013 However Quick ratio has declined in 2013 which indicates deteriorated Liqu...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


