In Equation 7.30 we showed that the amount an individual is willing to pay to avoid a fair gamble (h) is given by p =
In Equation 7.30 we showed that the amount an individual is willing to pay to avoid a fair gamble (h) is given by p = 0.5E(h 2 ) r(W), where r(W) is the measure of absolute risk aversion at this person's initial level of wealth. In this problem we look at the size of this payment as a function of the size of the risk faced and this person's level of wealth.
a. Consider a fair gamble (v) of winning or losing $1, For this gamble, what is E (v 2 )?
b. Now consider varying the gamble in part (a) by multiplying each prize by a positive constant k. Let h = kv. What is the value of E (h 2 )?
c. Suppose this person has a logarithmic utility function U (W) = In W. What is a general expression for r (W)?
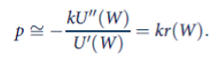
p=- KU" (W) U'(W) = kr(W).
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (144 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a A fair gamble is a specified set of prizes and asso...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
6091e6429a47d_22645.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
6091e6429a47d_22645.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


