Question
In order to study the photochemical decay of aqueous bromine in bright sunlight, a small quantity of liquid bromine was dissolved in water contained in
In order to study the photochemical decay of aqueous bromine in bright sunlight, a small quantity of liquid bromine was dissolved in water contained in a glass battery jar and placed in direct sunlight. The following data were obtained at 25?C:
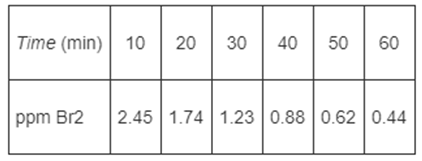
(a) Determine whether the reaction rate is zero, first, or second order in bromine, and calculate the reaction rate constant in units of your choice.
(b) Assuming identical exposure conditions, calculate the required hourly rate of injection of bromine (in pounds per hour) into a sunlit body of water, 25,000 gal in volume, in order to maintain a sterilizing level of bromine of 1.0 ppm.
(c) Apply one or more of the six ideas in Table to this problem. (Note: ppm = parts of bromine per million parts of brominated water by weight. In dilute aqueous solutions, 1 ppm = 1 milligram per liter.) (From California Professional Engineers' Exam.)
Table P-3 Practicing Creative Thinking

Time (min) 10 ppm Br2 20 30 40 50 60 2.45 1.74 1.23 0.88 0.62 0.44 (1) Brainstorm ideas to ask another question or suggest another calculation that can be made for this homework problem. (2) Brainstorm ways you could work this homework problem incorrectly. (3) Brainstorm ways to make this problem easier or more difficult or more exciting. (4) Brainstorm a list of things you learned from working this homework problem and what you think the point of the problem is. (5) Brainstorm the reasons why your calculations overpredicted the conversion that was measured when the reactor was put on stream. Assume you made no numerical errors on your calculations. (6) "What if..." questions: The "What if..." questions are particularly effective when used with the Living Example Problems, where one varies the parameters to explore the problem and to carry out a sensitivity analysis. For example, what if someone suggested that you should double the catalyst particle diameter, what would you say?
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a The stoichiometric rate of a reaction is as follows Here k is the specific reaction constant C A i...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
6095da305737b_26320.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
6095da305737b_26320.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


